HIV-specific T cell cytotoxicity mediated by RANTES via the chemokine receptor CCR3
- PMID: 9687538
- PMCID: PMC2212468
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.3.609
HIV-specific T cell cytotoxicity mediated by RANTES via the chemokine receptor CCR3
Abstract
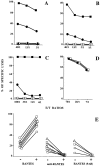
CC chemokines produced by CD8(+) T cells are known to act as HIV-suppressive factors. We studied the possible role of these chemokines in HIV-1-specific killing of target cells. We found that the activity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in CTL lines or freshly isolated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from HIV-1-infected individuals is markedly enhanced by RANTES (regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted) and virtually abolished by an antibody neutralizing RANTES or the RANTES receptor antagonist RANTES(9-68). Lysis was mediated by CD8(+) major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted T cells and was obtained with target cells expressing epitopes of the HIV-1LAI proteins Gag, Pol, Env, and Nef. The cytolytic activity observed in the presence or absence of added RANTES could be abolished by pretreatment of the CTLs with pertussis toxin, indicating that the effect is mediated by a G protein-coupled receptor. The chemokines monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-3, MCP-4, and eotaxin acted like RANTES, whereas macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1alpha, MIP-1beta, MCP-1, and stromal cell-derived factor 1 were inactive, suggesting a role for the eotaxin receptor, CCR3, and ruling out the involvement of CCR1, CCR2, CCR5, and CXCR4. CTL activity was abrogated by an antibody that blocks CCR3, further indicating that specific lysis is triggered via this chemokine receptor. These observations reveal a novel mechanism for the induction of HIV-1-specific cytotoxicity that depends on RANTES acting via CCR3.
Figures

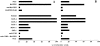

References
-
- Autran B, Hadida F, Haas G. Evolution and plasticity of CTL responses against HIV. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:546–553. - PubMed
-
- Gotch FM, Nixon DF, Alp N, McMichael AJ, Borysievicz LK. High frequency of memory and effector Gag-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in HIV seropositive individuals. Int Immunol. 1990;2:707–712. - PubMed
-
- Hoffenbach A, Langlade-Demoyen P, Vilmer E, Dadaglio G, Michel F, Mayaud C, Autran B, Plata F. Very high frequencies of HIV specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in humans. J Immunol. 1989;142:452–456. - PubMed
-
- Joly P, Guillon JM, Mayaud C, Plata F, Theodorou I, Denis M, Debré P, Autran B. Cell mediated suppression of HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989;143:2193–2201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

