Regulation of Ich-1 pre-mRNA alternative splicing and apoptosis by mammalian splicing factors
- PMID: 9689050
- PMCID: PMC21308
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9155
Regulation of Ich-1 pre-mRNA alternative splicing and apoptosis by mammalian splicing factors
Abstract
The importance of alternative splicing in regulating apoptosis has been suggested by findings of functionally antagonistic proteins generated by alternative splicing of several genes involved in apoptosis. Among these, Ich-1 (also named as caspase-2) encodes a member of the caspase family of proteases. Two forms of Ich-1 are produced as a result of alternative splicing: Ich-1L, which causes apoptosis, and Ich-1S, which prevents apoptosis. The precise nature of Ich-1 alternative splicing and its regulation remain unknown. Here, we show that the production of Ich-1L and Ich-1S transcripts results from alternative exclusion or inclusion of a 61-bp exon. Several splicing factors can regulate Ich-1 splicing. Serine-arginine-rich proteins SC35 and ASF/SF2 promote exon skipping, decreasing the ratio of Ich-1S to Ich-1L transcripts; whereas heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 facilitates exon inclusion, increasing this ratio. Furthermore, in cultured cells, SC35 overexpression increases apoptosis; whereas heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 overexpression decreases apoptosis. These results provide the first direct evidence that splicing factors can regulate Ich-1 alternative splicing and suggest that alternative splicing may be an important regulatory mechanism for apoptosis.
Figures
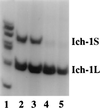



References
-
- Boise L H, González-García M, Postema C E, Ding L, Lindstein T, Turka L A, Mao X, Nuñez G, Thompson C B. Cell. 1993;74:597–608. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Miura M, Bergeron L, Zhu H, Yuan J-Y. Cell. 1994;78:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Shaham S, Horvitz H R. Cell. 1996;86:201–208. - PubMed
-
- Alnemri E S, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:4312–4317. - PubMed
-
- Papoff G, Cascino I, Eramo A, Starace G, Lynch D H, Ruberti G. J Immunol. 1996;156:4622–4630. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

