cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates and activates nuclear Ca2+-ATPase
- PMID: 9689054
- PMCID: PMC21312
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9178
cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates and activates nuclear Ca2+-ATPase
Abstract
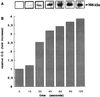
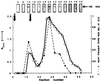
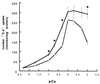
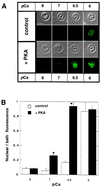
A Ca2+-pump ATPase, similar to that in the endoplasmic reticulum, has been located on the outer membrane of rat liver nuclei. The effect of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) on nuclear Ca2+-ATPase (NCA) was studied by using purified rat liver nuclei. Treatment of isolated nuclei with the catalytic unit of PKA resulted in the phosphorylation of a 105-kDa band that was recognized by antibodies specific for sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase type 2b. Partial purification and immunoblotting confirmed that the 105-kDa protein band phosphorylated by PKA is NCA. The stoichiometry of phosphorylation was 0.76 mol of phosphate incorporated/mol of partially purified enzyme. Measurement of ATP-dependent 45Ca2+ uptake into purified nuclei showed that PKA phosphorylation enhanced the Ca2+-pumping activity of NCA. We show that PKA phosphorylation of Ca2+-ATPase enhances the transport of 10-kDa fluorescent-labeled dextrans across the nuclear envelope. The findings reported in this paper are consistent with the notion that the crosstalk between the cAMP/PKA- and Ca2+-dependent signaling pathways identified at the cytoplasmic level extends to the nucleus. Furthermore, these data support a function for crosstalk in the regulation of calcium-dependent transport across the nuclear envelope.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

