Mutation of the polo-box disrupts localization and mitotic functions of the mammalian polo kinase Plk
- PMID: 9689075
- PMCID: PMC21333
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9301
Mutation of the polo-box disrupts localization and mitotic functions of the mammalian polo kinase Plk
Abstract
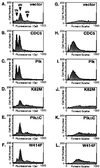
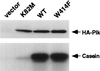
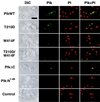
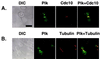
Members of the polo subfamily of protein kinases play pivotal roles in cell proliferation. In addition to the kinase domain, polo kinases have a strikingly conserved sequence in the noncatalytic domain, termed the polo-box. The function of the polo-box is currently undefined. The mammalian polo-like kinase Plk is a functional homologue of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cdc5. Here, we show that Plk localizes at the spindle poles and cytokinetic neck filaments. Without impairing kinase activity, a conservative mutation in the polo-box disrupts the capacity of Plk to complement the defect associated with a cdc5-1 temperature-sensitive mutation and to localize to these subcellular structures. Our data provide evidence that the polo-box plays a critical role in Plk function, likely by directing its subcellular localization.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

