Protection against lipoapoptosis of beta cells through leptin-dependent maintenance of Bcl-2 expression
- PMID: 9689119
- PMCID: PMC21377
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.16.9558
Protection against lipoapoptosis of beta cells through leptin-dependent maintenance of Bcl-2 expression
Abstract
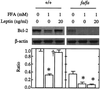
Obesity causes its complications through functional and morphologic damage to remotely situated tissues via undetermined mechanisms. In one rodent model of obesity, the Zucker diabetic fatty fa/fa rat, overaccumulation of triglycerides in the pancreatic islets may be responsible for a gradual depletion of beta cells, leading to the most common complication of obesity, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. At the onset of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, the islets from fa/fa rats contain up to 100 times the fat content of islets from normal lean rats. Ultimately, about 75% of the beta cells disappear from these fat-laden islets as a consequence of apoptosis induced by long-chain fatty acids (FA). Here we quantify Bcl-2, the anti-apoptosis factor in these islets, and find that Bcl-2 mRNA and protein are, respectively, 85% and 70% below controls. In normal islets cultured in 1 mM FA, Bcl-2 mRNA declined by 68% and completely disappeared in fa/fa islets cultured in FA. In both groups, suppression was completely blocked by the fatty acyl-CoA synthetase inhibitor, triacsin C, evidence of its mediation by fatty acyl-CoA. To determine whether leptin action blocked FA-induced apoptosis, we cultured normal and fa/fa islets in 1 mM FA with or without leptin. Leptin completely blocked FA-induced Bcl-2 suppression in normal islets but had no effect on islets from fa/fa rats, which are unresponsive to leptin because of a mutation in their leptin receptors (OB-R). However, when wild-type OB-R is overexpressed in fa/fa islets, leptin completely prevented FA-induced Bcl-2 suppression and DNA fragmentation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipoapoptosis in beta-cells of obese prediabetic fa/fa rats. Role of serine palmitoyltransferase overexpression.J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 4;273(49):32487-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.49.32487. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9829981
-
Overexpression of leptin receptors in pancreatic islets of Zucker diabetic fatty rats restores GLUT-2, glucokinase, and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Sep 29;95(20):11921-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.20.11921. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9751766 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin normalizes the impaired response of proinsulin mRNA to long chain fatty acids in heterozygous Zucker diabetic fatty rats.J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 10;272(41):25648-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.41.25648. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9325287
-
Lipotoxic diseases of nonadipose tissues in obesity.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000 Nov;24 Suppl 4:S28-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0801498. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2000. PMID: 11126236 Review.
-
Lipoapoptosis: its mechanism and its diseases.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Dec 30;1585(2-3):202-12. doi: 10.1016/s1388-1981(02)00342-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12531555 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased beta-cell mass in diabetes: significance, mechanisms and therapeutic implications.Diabetologia. 2004 Mar;47(3):581-589. doi: 10.1007/s00125-004-1336-4. Epub 2004 Feb 7. Diabetologia. 2004. PMID: 14767595 Review.
-
Growth hormone receptor antagonist transgenic mice are protected from hyperinsulinemia and glucose intolerance despite obesity when placed on a HF diet.Endocrinology. 2015 Feb;156(2):555-64. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1617. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25406017 Free PMC article.
-
PPARGC1A rs3736265 G>A polymorphism is associated with decreased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus and fasting plasma glucose level.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 6;8(23):37308-37320. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16307. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28418876 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of p38 MAPK and JNK via Akt-mediated inhibition of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 constitutes a core component of the beta-cell pro-survival effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.J Biol Chem. 2009 Oct 30;284(44):30372-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.060178. Epub 2009 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19748889 Free PMC article.
-
T cells cooperate with palmitic acid in induction of beta cell apoptosis.BMC Immunol. 2009 May 22;10:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-10-29. BMC Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19463182 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

