Sorivudine and 5-fluorouracil; a clinically significant drug-drug interaction due to inhibition of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase
- PMID: 9690942
- PMCID: PMC1873978
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00050.x
Sorivudine and 5-fluorouracil; a clinically significant drug-drug interaction due to inhibition of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase
Abstract
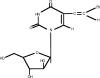
Sorivudine (1-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-E-5-[2-bromovinyl] uracil; BV-araU; SQ32,756) is an antimetabolite which is a synthetic analogue of thymidine. This drug has demonstrated antiviral activity against varicella zoster virus, herpes simplex type 1 virus, and Epstein-Barr virus. Clinical studies in Japan and subsequently worldwide showed this drug to be a potent agent for treating varicella zoster infections. Although in general well tolerated, a fatal drug interaction with fluoropyrimidine drugs was subsequently observed. While three deaths resulting from this interaction were recognized to have occurred during the initial clinical evaluation in Japan, the full impact of the interaction was not recognized in Japan until post-marketing when an additional 23 cases of severe toxicity were reported including 16 patients who subsequently died from fluoro-pyrimidine toxicity. Worldwide recognition of this potentially fatal drug-drug interaction led to subsequent disapproval in the US and elsewhere. The interaction has been shown to be due to suppression of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) catabolism, resulting in higher levels of 5-FU than would normally be observed. The mechanism of this interaction is mediated through inhibition of the 5-FU rate-limiting catabolizing enzyme dihydropyrmidine dehydrogenase (DPD) by the BV-araU metabolite BVU. This drug-drug interaction of sorivudine and 5-FU further emphasizes the critical importance of DPD on the clinical pharmacology of 5-FU.
Figures

References
-
- Diasio RB. Principles of Drug Therapy. In: Bennett JC, Plum F, editors. Cecil Textbook of Medicine. 20. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company; 1996. Chapter 5.
-
- Machida H, Nishitani M. Drug susceptibilities of isolates of varicella-zoster virus in a clinical study of oral brovavir. Microbiol Immunol. 1990;34:407–411. - PubMed
-
- Whitley RJ. Sorivudine: a promising drug for the treament of varicella-zoster virus infection. Neurology. 1995;45:73–75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

