Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human interleukin-2 in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients following subcutaneous application
- PMID: 9690943
- PMCID: PMC1873983
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1998.00036.x
Pharmacokinetics of recombinant human interleukin-2 in advanced renal cell carcinoma patients following subcutaneous application
Abstract
Aims: The aim of the study was to investigate the pharmacokinetics of recombinant human interleukin-2 (rhIL-2) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma following different subcutaneous (s.c.) administration regimens.
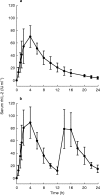
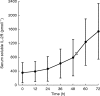
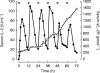
Methods: RhIL-2 was administered subcutaneously to 10 patients according to two different dosing regimens: group A received 20 x 10(6) IU m(-2) once daily and group B 10 x 10(6) IU m(-2) twice daily (every 12 h). Additionally, in all patients the influence of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) on the pharmacokinetics of rhIL-2 was investigated.
Results: The mean area under the serum concentration-time curve to 24 h (AUC(0,24 h)) was 627 IU ml(-1) h in treatment group A and 1130 IU ml(-1) h (P=0.029) in treatment group B. In both study groups Cmax and AUC(0,12 h) were not significantly different. Seventy-two hours after the beginning of s.c. rhIL-2 therapy the sIL-2R increased significantly (P=0.016), and sIL-2R levels over 1200 pmol l(-1) seemed to reduce the AUC.
Conclusions: In patients with metastatic renal cell cancer administration of 20 x 10(6) IU m(-2) of rhIL-2 s.c. in two daily doses (10 x 10(6) IU m(-2) every 12 h) provides better bioavailability and is preferable to the single dose administration.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenberg SA, Lotze MT, Muul LM, et al. A progress report on the treatment of 157 patients with advanced cancer using lymphokine-activated killer cells and interleukin-2 or high-dose interleukin-2 alone. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:889–897. - PubMed
-
- Atzpodien J, Körfer A, Franks C, Poliwoda H, Kirchner H. Home therapy with recombinant interleukin-2 and interferon-α2b in advanced human malignancies. Lancet. 1990;335:1509–1512. - PubMed
-
- Lotze MT, Grimm EA, Mazumder EA, Strausser JL, Rosenberg SA. Lysis of fresh and cultured autologous tumour by human lymphocytes cultured in T-cell growth factor. Cancer Res. 1981;41:4420–4425. - PubMed
-
- Atzpodien J, Körfer A, Evers P, et al. Low-dose subcutaneous recombinant interleukin-2 in advanced human malignancy: a phase II outpatient study. Mol Biother. 1990;2:18–26. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

