Molecular components of striatal plasticity: the various routes of cyclic AMP pathways
- PMID: 9691194
- PMCID: PMC4205584
- DOI: 10.1159/000017314
Molecular components of striatal plasticity: the various routes of cyclic AMP pathways
Abstract
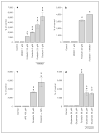
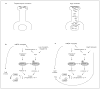
Neuroplasticity serves an important role for normal striatal function and in disease states. One route to neuroplasticity involves activation of the transcription factor cyclic 3', 5'-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) response element binding protein (CREB) by phosphorylation of the amino acid 133Ser. Dopamine and glutamate, the two predominant neurotransmitters in the striatum, induce CREB phosphorylation in primary cultures of rat striatum through cyclic AMP and Ca2+ pathways. Here we present the role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and Ca2+ in cyclic AMP-mediated CREB phosphorylation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Dopamine D2-like antagonists induce chromatin remodeling in striatal neurons through cyclic AMP-protein kinase A and NMDA receptor signaling.J Neurochem. 2004 Sep;90(5):1117-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02569.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15312167 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular basis of dopamine and glutamate interactions in the striatum.Adv Pharmacol. 1998;42:729-33. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60851-0. Adv Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9328002 No abstract available.
-
Region-dependent dynamics of cAMP response element-binding protein phosphorylation in the basal ganglia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Apr 14;95(8):4708-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4708. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9539803 Free PMC article.
-
Food restriction increases NMDA receptor-mediated calcium-calmodulin kinase II and NMDA receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-mediated cyclic amp response element-binding protein phosphorylation in nucleus accumbens upon D-1 dopamine receptor stimulation in rats.Neuroscience. 2005;132(4):1035-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.02.006. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15857708
-
L-type Ca2+ channel blockers promote Ca2+ accumulation when dopamine receptors are activated in striatal neurons.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004 Nov 24;131(1-2):65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.08.007. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15530653 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Drug-induced activation of dopamine D(1) receptor signaling and inhibition of class I/II histone deacetylase induce chromatin remodeling in reward circuitry and modulate cocaine-related behaviors.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008 Nov;33(12):2981-92. doi: 10.1038/npp.2008.15. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008. PMID: 18288092 Free PMC article.
-
L-Type Ca(2+) channels are essential for glutamate-mediated CREB phosphorylation and c-fos gene expression in striatal neurons.J Neurosci. 1999 Aug 1;19(15):6348-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-15-06348.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10414964 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of dopamine receptors in the developing medial frontal cortex and striatum of the rat.Neuroscience. 2011 Dec 29;199:501-14. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.10.004. Epub 2011 Oct 8. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 22015925 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D2-like antagonists induce chromatin remodeling in striatal neurons through cyclic AMP-protein kinase A and NMDA receptor signaling.J Neurochem. 2004 Sep;90(5):1117-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02569.x. J Neurochem. 2004. PMID: 15312167 Free PMC article.
-
Psychostimulants, Protein phosphorylation and Gene expression: a growing role of L-type calcium channels.Cellscience. 2005 Jul 29;2(1):127-144. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2005.2-127. Cellscience. 2005. PMID: 16724157 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Matthies H. In search of cellular mechanisms of memory. Prog Neurobiol. 1989;32:277–349. - PubMed
-
- Deadwyler SA, Dunwiddie T, Lynch G. A critical level of protein synthesis is required for long-term potentiation. Synapse. 1987;1:90–95. - PubMed
-
- Schulman H. Protein phosphorylation in neuronal plasticity and gene expression. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995;5:375–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

