Distinct C/EBP functions are required for eosinophil lineage commitment and maturation
- PMID: 9694805
- PMCID: PMC317049
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.15.2413
Distinct C/EBP functions are required for eosinophil lineage commitment and maturation
Abstract
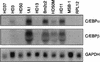
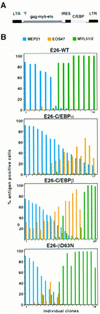
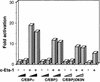
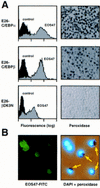
Hematopoietic differentiation involves the commitment of multipotent progenitors to a given lineage, followed by the maturation of the committed cells. To study the transcriptional events controlling these processes, we have investigated the role of C/EBP proteins in lineage choice of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors (MEPs) transformed by the E26 virus. We found that forced expression of either the alpha or beta isoforms of C/EBP in MEPs induced eosinophil differentiation and that in addition, C/EBPbeta could induce myeloid differentiation. Conversely, dominant-negative versions of C/EBPbeta inhibited myeloid differentiation. C/EBP-induced eosinophil differentiation could be separated into two distinct events, lineage commitment and maturation. Thus, eosinophils induced by transactivation-deficient C/EBPbeta alleles were found to be blocked in their maturation, whereas those expressing wild-type C/EBP proteins were not. Likewise, a 1-day activation of a conditional C/EBPbeta allele in multipotent progenitors led to the formation of immature eosinophils, whereas sustained activation produced mature eosinophils. These results show that C/EBP can induce both myeloid and eosinophil lineage commitment and that transactivation independent and dependent C/EBP functions are required during eosinophil lineage commitment and maturation, respectively.
Figures


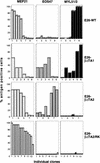
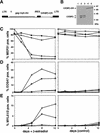
 ) E26–βERcl.1; (⋄) E26–βERcl.2.
) E26–βERcl.1; (⋄) E26–βERcl.2.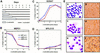
References
-
- Akiyama Y, Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek’s desease. Biken J. 1974;17:105–116. - PubMed
-
- Beug H, von Kirchbach A, Döderlein G, Conscience J-F, Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979;18:375–390. - PubMed
-
- Beug, H., G. Doederlein, C. Freudenstein, and T. Graf. 1982. Erythroblast cell lines transformed by a temperature sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus: A model system to study erythroid differentiation in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. (Suppl.) 1: 195–207. - PubMed
-
- Beug H, Leutz A, Kahn P, Graf T. Ts mutants of E26 leukemia virus allow transformed myeloblasts, but not erythroblasts or fibroblasts, to differentiate at the nonpermissive temperature. Cell. 1984;39:579–588. - PubMed
-
- Brune K, Spitznagel JK. Peroxidaseless chicken leukocytes: Isolation and characterization of antibacterial granules. J Infect Dis. 1973;127:84–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
