Myc signaling via the ARF tumor suppressor regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and immortalization
- PMID: 9694806
- PMCID: PMC317045
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.15.2424
Myc signaling via the ARF tumor suppressor regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and immortalization
Abstract
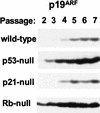
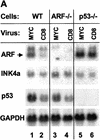
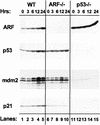
Establishment of primary mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs) as continuously growing cell lines is normally accompanied by loss of the p53 or p19(ARF) tumor suppressors, which act in a common biochemical pathway. myc rapidly activates ARF and p53 gene expression in primary MEFs and triggers replicative crisis by inducing apoptosis. MEFs that survive myc overexpression sustain p53 mutation or ARF loss during the process of establishment and become immortal. MEFs lacking ARF or p53 exhibit an attenuated apoptotic response to myc ab initio and rapidly give rise to cell lines that proliferate in chemically defined medium lacking serum. Therefore, ARF regulates a p53-dependent checkpoint that safeguards cells against hyperproliferative, oncogenic signals.
Figures

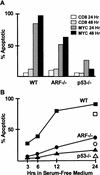

 ). A significant number of myc-infected
ARF-null and p53-null cells survived in serum-free
conditions (B, C,
). A significant number of myc-infected
ARF-null and p53-null cells survived in serum-free
conditions (B, C,  ). When reseeded 14 days postinfection, these
myc-infected cells grew continuously in serum-free medium
(B,C, ▵). All data points represent averages of six to
eight determinations using at least three independently derived MEF
strains with
). When reseeded 14 days postinfection, these
myc-infected cells grew continuously in serum-free medium
(B,C, ▵). All data points represent averages of six to
eight determinations using at least three independently derived MEF
strains with 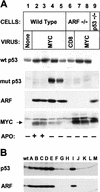
References
-
- Askew DS, Ashmun RA, Simmons BC, Cleveland JL. Constitutive c-mycexpression in an IL3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991;6:1915–1922. - PubMed
-
- Debbas M, White E. Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes & Dev. 1993;7:546–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
