E1A signaling to p53 involves the p19(ARF) tumor suppressor
- PMID: 9694807
- PMCID: PMC317046
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.15.2434
E1A signaling to p53 involves the p19(ARF) tumor suppressor
Abstract
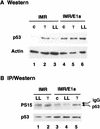
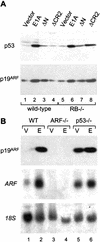
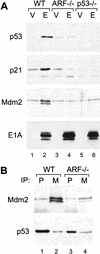
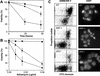
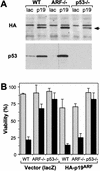
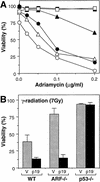
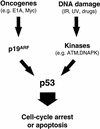
The adenovirus E1A oncogene activates p53 through a signaling pathway involving the retinoblastoma protein and the tumor suppressor p19(ARF). The ability of E1A to induce p53 and its transcriptional targets is severely compromised in ARF-null cells, which remain resistant to apoptosis following serum depletion or adriamycin treatment. Reintroduction of p19(ARF) restores p53 accumulation and resensitizes ARF-null cells to apoptotic signals. Therefore, p19(ARF) functions as part of a p53-dependent failsafe mechanism to counter uncontrolled proliferation. Synergistic effects between the p19(ARF) and DNA damage pathways in inducing p53 may contribute to E1A's ability to enhance radio- and chemosensitivity.
Figures
References
-
- Andree HA, Reutelingsperger CP, Hauptmann R, Hemker HC, Hermens WT, Willems GM. Binding of vascular anticoagulant alpha (VAC alpha) to planar phospholipid bilayers. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:4923–4928. - PubMed
-
- Barak Y, Gottlieb E, Juvengershon T, Oren M. Regulation of mdm2 expression by p53: Alternative promoters produce transcripts with nonidentical translation potential. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:1739–1749. - PubMed
-
- Debbas M, White E. Wild-type p53 mediates apoptosis by E1A, which is inhibited by E1B. Genes & Dev. 1993;7:546–554. - PubMed
-
- DeCaprio JA, Ludlow JW, Lynch D, Furukawa Y, Griffin J, Piwnica-Worms H, Huang CM, Livingstone DM. SV40 large T antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988;54:275–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
