Phosphate assimilation in Rhizobium (Sinorhizobium) meliloti: identification of a pit-like gene
- PMID: 9696772
- PMCID: PMC107420
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.16.4219-4226.1998
Phosphate assimilation in Rhizobium (Sinorhizobium) meliloti: identification of a pit-like gene
Abstract
Rhizobium meliloti mutants defective in the phoCDET-encoded phosphate transport system form root nodules on alfalfa plants that fail to fix nitrogen (Fix-). We have previously reported that two classes of second-site mutations can suppress the Fix- phenotype of phoCDET mutants to Fix+. Here we show that one of these suppressor loci (sfx1) contains two genes, orfA and pit, which appear to form an operon transcribed in the order orfA-pit. The Pit protein is homologous to various phosphate transporters, and we present evidence that three suppressor mutations arose from a single thymidine deletion in a hepta-thymidine sequence centered 54 nucleotides upstream of the orfA transcription start site. This mutation increased the level of orfA-pit transcription. These data, together with previous biochemical evidence, show that the orfA-pit genes encode a Pi transport system that is expressed in wild-type cells grown with excess Pi but repressed in cells under conditions of Pi limitation. In phoCDET mutant cells, orfA-pit expression is repressed, but this repression is alleviated by the second-site suppressor mutations. Suppression increases orfA-pit expression compensating for the deficiencies in phosphate assimilation and symbiosis of the phoCDET mutants.
Figures
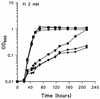
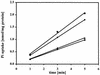
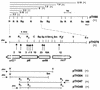

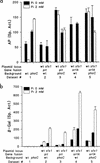
References
-
- Bieleski R L. Phosphate pools, phosphate transport, and phosphate availability. Annu Rev Plant Physiol. 1973;24:225–252.
-
- Bollinger J M, Jr, Kwon D S, Huisman G W, Kolter R, Walsh C T. Glutathionylspermidine metabolism in Escherichia coli. Purification, cloning, overproduction, and characterization of a bifunctional glutathionylspermidine synthetase/amidase. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:14031–14041. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

