Functional region IV of glycoprotein D from herpes simplex virus modulates glycoprotein binding to the herpesvirus entry mediator
- PMID: 9696802
- PMCID: PMC109930
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7091-7098.1998
Functional region IV of glycoprotein D from herpes simplex virus modulates glycoprotein binding to the herpesvirus entry mediator
Abstract
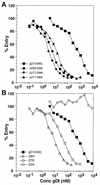
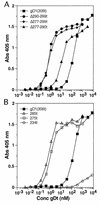
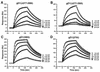
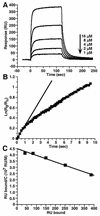
Glycoprotein D (gD) of herpes simplex virus (HSV) is essential for virus entry and has four functional regions (I to IV) important for this process. We previously showed that a truncated form of a functional region IV variant, gD1(Delta290-299t), had an enhanced ability to block virus entry and to bind to the herpesvirus entry mediator (HveAt; formerly HVEMt), a cellular receptor for HSV. To explore this phenotype further, we examined other forms of gD, especially ones with mutations in region IV. Variant proteins with deletions of amino acids between 277 and 300 (region IV), as well as truncated forms lacking C-terminal residues up to amino acid 275 of gD, were able to block HSV entry into Vero cells 1 to 2 logs better than wild-type gD1(306t). In contrast, gD truncated at residue 234 did not block virus entry into Vero cells. Using optical biosensor technology, we recently showed that gD1(Delta290-299t) had a 100-fold-higher affinity for HveAt than gD1(306t) (3.3 x 10(-8) M versus 3.2 x 10(-6) M). Here we found that the affinities of other region IV variants for HveAt were similar to that of gD1(Delta290-299t). Thus, the affinity data follow the same hierarchy as the blocking data. In each case, the higher affinity was due primarily to a faster kon rather than to a slower koff. Therefore, once the gDt-HveAt complex formed, its stability was unaffected by mutations in or near region IV. gD truncated at residue 234 bound to HveAt with a lower affinity (2.0 x 10(-5) M) than did gD1(306t) due to a more rapid koff. These data suggest that residues between 234 and 275 are important for maintaining stability of the gDt-HveAt complex and that functional region IV is important for modulating the binding of gD to HveA. The binding properties of any gD1(234t)-receptor complex could account for the inability of this form of gDt to block HSV infection.
Figures


References
-
- Biacore AB. BIAevaluation software handbook, version 3.0. Uppsala, Sweden: Biacore AB; 1997.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

