The ability of positive transcription elongation factor B to transactivate human immunodeficiency virus transcription depends on a functional kinase domain, cyclin T1, and Tat
- PMID: 9696809
- PMCID: PMC109937
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7154-7159.1998
The ability of positive transcription elongation factor B to transactivate human immunodeficiency virus transcription depends on a functional kinase domain, cyclin T1, and Tat
Abstract
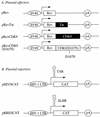
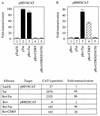
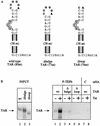
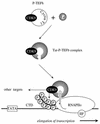
By binding to the transactivation response element (TAR) RNA, the transcriptional transactivator (Tat) from the human immunodeficiency virus increases rates of elongation rather than initiation of viral transcription. Two cyclin-dependent serine/threonine kinases, CDK7 and CDK9, which phosphorylate the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, have been implicated in Tat transactivation in vivo and in vitro. In this report, we demonstrate that CDK9, which is the kinase component of the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) complex, can activate viral transcription when tethered to the heterologous Rev response element RNA via the regulator of expression of virion proteins (Rev). The kinase activity of CDK9 and cyclin T1 is essential for these effects. Moreover, P-TEFb binds to TAR only in the presence of Tat. We conclude that Tat-P-TEFb complexes bind to TAR, where CDK9 modifies RNA polymerase II for the efficient copying of the viral genome.
Figures

References
-
- Akoulitchev S, Makela T P, Weinberg R A, Reinberg D. Requirement for TFIIH kinase activity in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1995;377:557–560. - PubMed
-
- Aso T, Conaway J W, Conaway R C. The RNA polymerase II elongation complex. FASEB J. 1995;9:1419–1428. - PubMed
-
- Bentley D L. Regulation of transcriptional elongation by RNA polymerase II. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995;5:210–216. - PubMed
-
- Bullrich F, MacLachlan T K, Sang N, Druck T, Veronese M L, Allen S L, Chiorazzi N, Koff A, Heubner K, Croce C M, Giordano A. Chromosomal mapping of members of the cdc2 family of protein kinases, cdk3, cdk6, PISSLRE, and PITALRE, and a cdk inhibitor, p27Kip1, to regions involved in human cancer. Cancer Res. 1995;55:1199–1205. - PubMed
-
- Caputo A, Grossi M P, Bozzini R, Rossi C, Betti M, Marconi P C, Barbanti-Brodano G, Balboni P G. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication and reactivation from latency by tat transdominant negative mutants in the cysteine rich region. Gene Ther. 1996;3:235–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

