Binding of Sindbis virus to cell surface heparan sulfate
- PMID: 9696831
- PMCID: PMC109959
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7349-7356.1998
Binding of Sindbis virus to cell surface heparan sulfate
Abstract
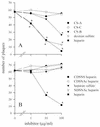
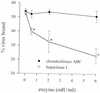
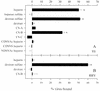
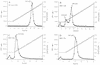
Alphaviruses are arthropod-borne viruses with wide species ranges and diverse tissue tropisms. The cell surface receptors which allow infection of so many different species and cell types are still incompletely characterized. We show here that the widely expressed glycosaminoglycan heparan sulfate can participate in the binding of Sindbis virus to cells. Enzymatic removal of heparan sulfate or the use of heparan sulfate-deficient cells led to a large reduction in virus binding. Sindbis virus bound to immobilized heparin, and this interaction was blocked by neutralizing antibodies against the viral E2 glycoprotein. Further experiments showed that a high degree of sulfation was critical for the ability of heparin to bind Sindbis virus. However, Sindbis virus was still able to infect and replicate on cells which were completely deficient in heparan sulfate, indicating that additional receptors must be involved. Cell surface binding of another alphavirus, Ross River virus, was found to be independent of heparan sulfate.
Figures



References
-
- Bose H R, Carl G Z, Sagik B P. Separation of Sindbis virus plaque-type variants by calcium phosphate chromatography. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;29:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Brown L N, Packer R A. Some factors affecting plaque size of western equine encephalomyelitis virus. Am J Vet Res. 1964;25:487–493. - PubMed
-
- Byrnes, A. P., and D. E. Griffin. Unpublished data.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

