Migration of mitochondria to viral assembly sites in African swine fever virus-infected cells
- PMID: 9696857
- PMCID: PMC110008
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7583-7588.1998
Migration of mitochondria to viral assembly sites in African swine fever virus-infected cells
Abstract
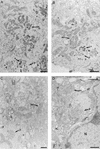
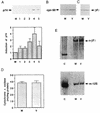
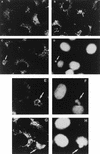
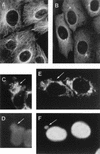
An examination by electron microscopy of the viral assembly sites in Vero cells infected with African swine fever virus showed the presence of large clusters of mitochondria located in their proximity. These clusters surround viral factories that contain assembling particles but not factories where only precursor membranes are seen. Immunofluorescence microscopy revealed that these accumulations of mitochondria are originated by a massive migration of the organelle to the virus assembly sites. Virus infection also promoted the induction of the mitochondrial stress-responsive proteins p74 and cpn 60 together with a dramatic shift in the ultrastructural morphology of the mitochondria toward that characteristic of actively respiring organelles. The clustering of mitochondria around the viral factory was blocked in the presence of the microtubule-disassembling drug nocodazole, indicating that these filaments are implicated in the transport of the mitochondria to the virus assembly sites. The results presented are consistent with a role for the mitochondria in supplying the energy that the virus morphogenetic processes may require and make of the African swine fever virus-infected cell a paradigm to investigate the mechanisms involved in the sorting of mitochondria within the cell.
Figures

References
-
- Alconada A, Flores A I, Blanco L, Cuezva J M. Antibodies against F1-ATPase α-subunit recognize mitochondrial chaperones. Evidence for an evolutionary relationship between chaperonin and ATPase protein families. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:13670–13679. - PubMed
-
- Andrés, G. Personal communication.
-
- Brady S T. A novel brain ATPase with properties expected for the fast axonal transport motor. Nature. 1985;317:73–75. - PubMed
-
- Brady S T, Lasek R J, Allen R D. Fast axonal transport in extruded axoplasm from squid giant axon. Science. 1982;218:1129–1131. - PubMed

