The nucleolus is the site of Borna disease virus RNA transcription and replication
- PMID: 9696879
- PMCID: PMC110048
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.9.7697-7702.1998
The nucleolus is the site of Borna disease virus RNA transcription and replication
Abstract
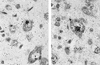
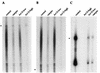
Borna disease virus (BDV) is a neurotropic nonsegmented negative-strand RNA virus with limited homology to rhabdoviruses and paramyxoviruses. A distinguishing feature of BDV is that it replicates in the nucleus of infected cells. Strand-specific probes used for in situ hybridization of infected rat brain showed that there was differential localization of positive- and negative-strand RNAs within the nucleus of neurons. Within nuclei, sense-strand RNAs were preferentially localized within nucleolar regions while genomic-sense RNAs were found in both nucleolar and nonnucleolar regions. These results suggested a role for the nucleolus in BDV replication. Nucleoli isolated from persistently infected neuroblastoma cells contained both genomic and antigenomic BDV RNA species as well as an enrichment of the 39/38-kDa and gp18 BDV proteins. Since the nucleolus is the site of rRNA transcription, we examined BDV transcription in the presence of inhibitors of RNA polymerase I. Inhibition of RNA polymerase I did not affect levels of BDV transcription.
Figures
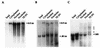
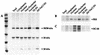
References
-
- Adachi Y, Copeland T D, Hatanaka M, Oroszlan S. Nucleolar targeting signal of rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I specifically binds to nucleolar shuttle protein B-23. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:13930–13934. - PubMed
-
- Biedler J L, Helson L, Spengler B A. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity, and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973;33:2643–2652. - PubMed
-
- Borer R A, Lehner C F, Eppenberger H M, Nigg E A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989;56:379–390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

