Neuronal expression of the 5HT3 serotonin receptor gene requires nuclear factor 1 complexes
- PMID: 9698312
- PMCID: PMC6793193
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-16-06186.1998
Neuronal expression of the 5HT3 serotonin receptor gene requires nuclear factor 1 complexes
Abstract
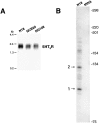
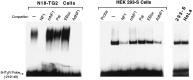
The 5HT3 receptor (5HT3R) is a serotonin-gated ion channel whose expression is restricted to a subset of cells within the central and peripheral nervous systems. In vitro analysis shows that a small proximal region of the TATA-less 5HT3R promoter is sufficient to direct neuronal-specific reporter gene expression. Three potential regulatory elements conserved between the mouse and human genes were identified within this proximal promoter, two of which are known sites for the ubiquitously expressed factors Sp1 and nuclear factor 1 (NF1). Surprisingly, mutation of the NF1 binding site abolished all reporter activity in cell transfection studies, suggesting that this element is essential for neuronal-specific transcriptional activity of the 5HT3R. Furthermore, a complex of neuronal proteins that includes a member(s) of the NF1 family binds to this site, as shown by gel mobility super shift and DNaseI footprinting analyses. Although NF1 has been proposed to mediate basal transcription of many ubiquitously expressed genes, our data suggest that a member of the NF1 transcription factor family participates in neuronal-specific gene expression by promoting interactions with other regulatory factors found in sensory ganglia.
Figures




Similar articles
-
SF-1 (steroidogenic factor-1), C/EBPbeta (CCAAT/enhancer binding protein), and ubiquitous transcription factors NF1 (nuclear factor 1) and Sp1 (selective promoter factor 1) are required for regulation of the mouse aldose reductase-like gene (AKR1B7) expression in adrenocortical cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2001 Jan;15(1):93-111. doi: 10.1210/mend.15.1.0577. Mol Endocrinol. 2001. PMID: 11145742
-
A negative regulatory element in the promoter region of the rat alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor gene overlaps an SP1 consensus binding site.Biochem J. 1995 Oct 15;311 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):541-7. doi: 10.1042/bj3110541. Biochem J. 1995. PMID: 7487893 Free PMC article.
-
Members of the nuclear factor 1 transcription factor family regulate rat 3alpha-hydroxysteroid/dihydrodiol dehydrogenase (3alpha-HSD/DD AKR1C9) gene expression: a member of the aldo-keto reductase superfamily.Mol Endocrinol. 1999 Oct;13(10):1704-17. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.10.0363. Mol Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 10517672
-
Identification of nuclear factor 1 (NF1) as a transcriptional modulator of rat A(2A) adenosine receptor.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003 Mar 17;111(1-2):61-73. doi: 10.1016/s0169-328x(02)00670-8. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12654506
-
Nuclear factor 1 family members mediate repression of the BK virus late promoter.Virology. 2001 Aug 15;287(1):89-104. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.1024. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11504545
Cited by
-
A genome-wide association study of seasonal pattern mania identifies NF1A as a possible susceptibility gene for bipolar disorder.J Affect Disord. 2013 Feb 20;145(2):200-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2012.07.032. Epub 2012 Aug 25. J Affect Disord. 2013. PMID: 22925353 Free PMC article.
-
Nfix Regulates Temporal Progression of Muscle Regeneration through Modulation of Myostatin Expression.Cell Rep. 2016 Mar 8;14(9):2238-2249. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.02.014. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26923583 Free PMC article.
-
Differential interactions of specific nuclear factor I isoforms with the glucocorticoid receptor and STAT5 in the cooperative regulation of WAP gene transcription.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;21(20):6859-69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.20.6859-6869.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11564870 Free PMC article.
-
The serotonin type 3A receptor facilitates luteinizing hormone release and LHbeta promoter activity in immortalized pituitary gonadotropes.Endocrine. 2005 Jun;27(1):37-43. doi: 10.1385/ENDO:27:1:037. Endocrine. 2005. PMID: 16077169
-
The transcriptional regulation of regucalcin gene expression.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Jan;346(1-2):147-71. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0601-8. Epub 2010 Oct 11. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20936536
References
-
- Cardinaux JR, Chapel S, Wahli W. Complex organization of CTF/NF-I, C/EBP, and HNF3 binding sites within the promoter of the liver-specific vitellogenin gene. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:32947–32956. - PubMed
-
- Chirgwin JJ, Przbyla AE, MacDonald RJ, Rutter WJ. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979;18:5294–5299. - PubMed
-
- Chong JA, Tapia RJ, Kim S, Toledo AJ, Zheng Y, Boutros MC, Altshuller YM, Frohman MA, Kraner SD, Mandel G. REST: a mammalian silencer protein that restricts sodium channel gene expression to neurons. Cell. 1995;80:949–957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
