Spatial regulation of exocytosis: lessons from yeast
- PMID: 9700152
- PMCID: PMC2148161
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.3.609
Spatial regulation of exocytosis: lessons from yeast
Figures
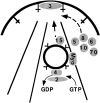
References
-
- Botstein, D., D. Amberg, J. Mulholland, T. Huffaker, A. Adams, D. Drubin and T. Stearns. The Yeast Cytoskeleton. In The Molecular and Cellular Biology of the Yeast Saccharomyces. J.R. Broach, J.R. Pringle, and E.W. Jones, editors. 1997. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. 1–90.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

