Interaptin, an actin-binding protein of the alpha-actinin superfamily in Dictyostelium discoideum, is developmentally and cAMP-regulated and associates with intracellular membrane compartments
- PMID: 9700162
- PMCID: PMC2148174
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.142.3.735
Interaptin, an actin-binding protein of the alpha-actinin superfamily in Dictyostelium discoideum, is developmentally and cAMP-regulated and associates with intracellular membrane compartments
Abstract
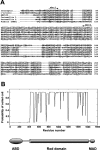
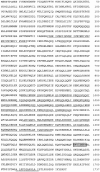
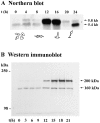
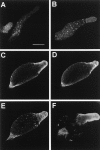
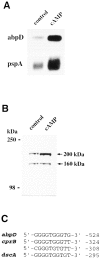
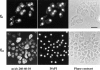
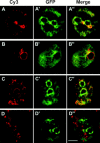
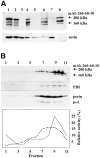
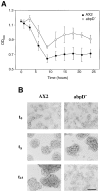
In a search for novel members of the alpha-actinin superfamily, a Dictyostelium discoideum genomic library in yeast artificial chromosomes (YAC) was screened under low stringency conditions using the acting-binding domain of the gelation factor as probe. A new locus was identified and 8.6 kb of genomic DNA were sequenced that encompassed the whole abpD gene. The DNA sequence predicts a protein, interaptin, with a calculated molecular mass of 204,300 D that is constituted by an actin-binding domain, a central coiled-coil rod domain and a membrane-associated domain. In Northern blot analyses a cAMP-stimulated transcript of 5.8 kb is expressed at the stage when cell differentiation occurs. Monoclonal antibodies raised against bacterially expressed interaptin polypeptides recognized a 200-kD developmentally and cAMP-regulated protein and a 160-kD constitutively expressed protein in Western blots. In multicellular structures, interaptin appears to be enriched in anterior-like cells which sort to the upper and lower cups during culmination. The protein is located at the nuclear envelope and ER. In mutants deficient in interaptin development is delayed, but the morphology of the mature fruiting bodies appears normal. When starved in suspension abpD- cells form EDTA-stable aggregates, which, in contrast to wild type, dissociate. Based on its domains and location, interaptin constitutes a potential link between intracellular membrane compartments and the actin cytoskeleton.
Figures
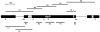


References
-
- Adachi H, Hasebe T, Yoshinaga K, Ohta T, Sutoh K. Isolation of Dictyostelium discoideumcytokinesis mutants by restriction enzyme-mediated integration of the blasticidin S resistance marker. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;205:1808–1814. - PubMed
-
- Beck KA, Buchanan JA, Nelson WJ. Golgi membrane skeleton: identification, localization and oligomerization of a 195 kD ankyrin isoform associated with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci. 1997;110:1239–1249. - PubMed
-
- Berthold J, Stadler J, Bozzaro S, Fichtner B, Gerisch G. Carbohydrate and other epitopes of the contact site A glycoprotein of Dictyostelium discoideumas characterized by monoclonal antibodies. Cell Differ. 1985;16:187–202. - PubMed
-
- Bennett H, Condeelis J. Isolation of an immunoreactive analogue of brain fodrin that is associated with the cell cortex of Dictyosteliumamoebae. Cell Motil Cytoskel. 1988;11:303–317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

