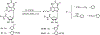Synthesis and biological activity of a new series of N6-arylcarbamoyl, 2-(Ar)alkynyl-N6-arylcarbamoyl, and N6-carboxamido derivatives of adenosine-5'-N-ethyluronamide as A1 and A3 adenosine receptor agonists
- PMID: 9703463
- PMCID: PMC9364910
- DOI: 10.1021/jm980147p
Synthesis and biological activity of a new series of N6-arylcarbamoyl, 2-(Ar)alkynyl-N6-arylcarbamoyl, and N6-carboxamido derivatives of adenosine-5'-N-ethyluronamide as A1 and A3 adenosine receptor agonists
Abstract
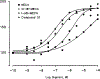
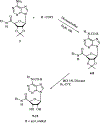
A new series of 1-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-deoxy-N-ethyl-beta-D-ribofuranuronamide++ +-b earing N-arylureas or N-arylcarboxamido groups at the purine 6 position and N-arylureas combined with halogens or alkynyl chains at the 2 position have been synthesized and tested for affinity at A1 and A2A adenosine receptors in rat brain membranes and at cloned rat A3 receptors expressed in CHO cells. The derivatives contained the 5' substituent found in the potent, nonselective agonist 1-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-1-deoxy-N-ethyl-beta-D-ribofuranuronamide++ + (NECA). While the carboxamido derivatives (9-13) showed affinity for A1 receptors, the urea derivatives (30-45) showed different degrees of affinity and selectivity for the A3 adenosine receptor subtype. In particular the derivative bearing a p-sulfonamidophenyl-urea at the 6 position, 31 showed a high affinity (Ki = 9 nM) and selectivity for the A3 receptors compared to that of the reference compound 1-[6-[[(3-iodophenyl)methyl]amino]-9H-purin-9-yl]-1-deoxy-N-methyl-be ta-D-ribofuranuronamide (IB-MECA). Furthermore, the importance of the stereochemistry in the interaction of these ligands at the rat A3 adenosine receptors has been evaluated by introducing a chiral chain at the 6 position. The introduction of halogens or alkynyl chains at the purine 2 position of selected ureas did not give the expected enhancement of potency at A2A and/or A3 receptors but rather showed a dramatic reduction of A2A affinity, resulting in compounds with good A2A/A3 selectivity. For example, the 2-(3-hydroxy-3-phenyl-1-propyn-1-yl)-6-(4-methoxyphenylurea) derivative 61 showed the capability to bind simultaneously to A1 and A3 receptor subtypes, excluding the A2A receptor. Compound 31 was shown to be an agonist, 9-fold more potent than NECA, at A3 receptors in rat RBL-2H3 mast cell membranes through stimulation of binding of [35S]GTP-gamma-S.
Figures
References
-
- Libert F; Schiffmann SN; Lefort A; Parmentier M; Gerard C; Dumont JE; Vanderhaeghen JJ; Vassart G The orphan receptor cDNA RDC7 encodes an A1 adenosine receptor. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 1677–1682. - PMC - PubMed
- Fredholm BB; Abbracchio MP; Burnstock G; Daly JW; Harden TK; Jacobson KA: Williams M Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol. Rev 1994, 46, 143–156. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Maenhaut C; Sande JV; Libert F; Abramowicz M; Parmentier M; Vanderhaeghen JJ; Dumont JE; Vassart G; Schiffmann S RDC8 codes for an adenosine A2 receptor with physiological constitutive activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1990, 173, 1169–1178. - PubMed
-
- Stehle JH; Rivkees SA; Lee JJ; Weaver DR; Deeds JD; Reppert SM Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel A2-adenosine receptor subtype. Mol. Endocrinol 1992, 6, 384–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials