Use of statins. Sheffield table is useful
- PMID: 9703541
- PMCID: PMC1113724
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.317.7156.473a
Use of statins. Sheffield table is useful
Figures
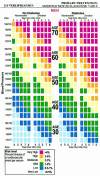

Comment on
-
Use of statins. Sheffield tables have shortcomings.BMJ. 1997 Dec 13;315(7122):1619. BMJ. 1997. PMID: 9437296 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Use of statins. Standing Medical Advisory Committee should reconsider advice to use Sheffield risk table.BMJ. 1997 Dec 13;315(7122):1620. BMJ. 1997. PMID: 9437298 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Use of statins [letters] BMJ. 1997;315:1615–1620. . (13 December.)
-
- Haq IU, Ramsay LE, Pickin DM, Yeo WW, Jackson PR, Payne JN. Lipid lowering for prevention of coronary heart disease: what policy now? Clin Sci. 1996;91:399–413. - PubMed
-
- Pyörälä K, De Backer G, Graham I, Poole-Wilson P, Wood D. Prevention of coronary heart disease in clinical practice. Recommendations of the task force of the European Atherosclerosis Society and European Society of Hypertension. Eur Heart J. 1994;15:1300–1331. - PubMed
-
- Haq IU, Jackson PR, Yeo WW, Ramsay LE. A comparison of methods for targeting CHD risk for primary prevention. Heart. 1997;77(suppl 1):36.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
