Interleukin-4 suppression of interleukin-1-induced transcription of collagenase (MMP-1) and stromelysin 1 (MMP-3) in human synovial fibroblasts
- PMID: 9704637
- PMCID: PMC1602062
- DOI: 10.1002/1529-0131(199808)41:8<1398::AID-ART8>3.0.CO;2-B
Interleukin-4 suppression of interleukin-1-induced transcription of collagenase (MMP-1) and stromelysin 1 (MMP-3) in human synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
Objective: To determine the effects of interleukin-4 (IL-4) on IL-1 induction of collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase 1 [MMP-1]) and stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) in human synovial fibroblasts.
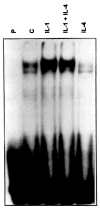
Methods: Northern blot analysis was performed to determine the effects of IL-4 on IL-1 induction of MMP messenger RNA (mRNA). MMP protein levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels were measured by enzyme immunoassay. Run-on transcription assays and transient transfection experiments were performed to determine whether the effects of IL-4 occur at the level of transcription. Activator protein 1 (AP-1) binding was assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay.
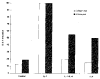
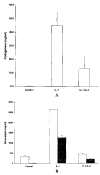
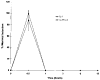
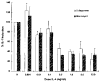
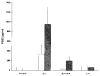
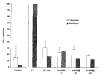
Results: Northern blot analysis revealed that coincubation of synovial fibroblasts with IL-1 and IL-4 resulted in a significant decrease in both collagenase and stromelysin mRNA levels compared with IL-1 alone, with a concomitant decrease in MMP protein levels. This inhibition is dose dependent, with an IC50 (50% inhibition concentration) for both MMPs of approximately 0.3 ng of IL-4 per ml, and is at least somewhat selective, since IL-1 induction of c-fos mRNA is not affected. Nuclear run-on experiments and transient transfection studies demonstrated that the suppression of IL-1-induced collagenase and stromelysin expression by IL-4 occurs at least in part at the transcriptional level, and that binding of transcription factor AP-1 is not affected. Although IL-1-induced levels of PGE2 are reduced by IL-4, exogenous addition of PGE2 does not abrogate the inhibitory effects of IL-4 on MMP expression.
Conclusion: IL-4 inhibits IL-1 induction of both collagenase and stromelysin, as well as PGE2 production, in human synovial fibroblasts. The inhibition occurs at least in part at the level of transcription, does not affect binding of transcription factor AP-1, and appears to involve a mechanism that is independent of the ability of IL-4 to inhibit production of PGE2.
Figures
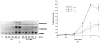
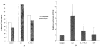
References
-
- Harris ED., Jr . Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Kelley WN, Harris ED Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge CB, editors. Textbook of rheumatolog. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1981. pp. 896–927.
-
- Birkedal-Hansen H. Role of cytokines and inflammatory mediators in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res. 1993;28:500–10. - PubMed
-
- MacNaul KL, Chartrain N, Lark M, Tocci MJ, Hutchinson NL. Discoordinate expression of stromelysin, collagenase, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases genes by prostaglandin E2. J Bid Chem. 1990;265:17238–45. - PubMed
-
- Mauviel A, Halcin C, Vasiloudes P, Parks WC, Kurkinen M, Uitto J. Uncoordinate regulation of collagenase, stromelysin, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases genes by prostaglandin E2: selective enhancement of collagenase gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts in culture. J Cell Biochem. 1994;54:465–72. - PubMed
-
- Yang M, Kurkinen M. Different mechanisms of regulation of the human stromelysin and collagenase genes: analysis by reverse-transcriptase-coupled PCR assay. Eur J Biochem. 1994;222:651–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

