Microsatellite markers for typing Aspergillus fumigatus isolates
- PMID: 9705365
- PMCID: PMC105135
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.9.2413-2418.1998
Microsatellite markers for typing Aspergillus fumigatus isolates
Abstract
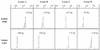
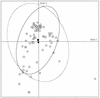
The use of microsatellites as highly polymorphic DNA markers for the typing of isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus was investigated. Four CA repeats were selected by screening an A. fumigatus DNA library with a (CA)10 oligonucleotide. Primers flanking these CA repeats were designed to amplify each locus. One primer of each pair was labeled with a fluorophore, and the PCR products were analyzed with an automatic sequencer and the GeneScan software. For each primer set and for a given isolate, one band was detected and was assigned to an allele because A. fumigatus is haploid. With 50 clinical isolates, 50 environmental isolates, and 2 reference strains we obtained 12, 11, 10, and 23 different alleles for the four CA microsatellites, respectively (discriminatory power, 0.994). The results were identical by whatever DNA extraction technique was used. Interestingly, no clustering between environmental and clinical isolates was observed, suggesting that every isolate is potentially pathogenic. Microsatellite markers appear suitable for use in large epidemiological studies of invasive aspergillosis.
Figures

References
-
- Backeljau T, De Bruyn L, De Wolf H, Jordaens K, Van Dongen S, Verhagen R, Winnepenninckx B. Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and parsimony methods. Cladistics. 1995;11:119–130. - PubMed
-
- Brownstein M J, Carpten J D, Smith J R. Modulation of non-templated nucleotide addition by Taq DNA polymerase: primer modifications that facilitate genotyping. BioTechniques. 1996;20:1004–1010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

