Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene
- PMID: 9705390
- PMCID: PMC105160
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.9.2548-2553.1998
Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene
Abstract
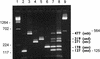
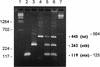
Two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays (PCR-EIAs) were developed for Staphylococcus aureus exotoxin gene screening as an alternative to the conventional biological assays, which depend on detectable amounts of toxins produced. One set of oligonucleotide primers and probes was designed to search for enterotoxin A to E genes (entA, entB, entC, entD, and entE), and the other one was designed to detect the staphylococcal exfoliative toxin genes (eta and etb) and the toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene (tst). Oligonucleotide primers were used as published previously, modified or newly developed to meet the requirements of both good size-distinguishable amplification bands of multiplex PCR and the temperature limit of the uracil DNA glycosylase system for carryover protection. Amplification products were visualized by agarose gel electrophoresis, and specificity was controlled with the aid of a DNA EIA system using oligonucleotide probes derived from the sequences of the S. aureus toxin genes. PCR procedures were performed by using template nucleic acids extracted from a panel of S. aureus reference strains and from a collection of 50 clinical strains. The PCR results were compared with those of immunological toxin production assays. This multiplex PCR-EIA system offers an alternative method for the rapid, sensitive, specific, and simultaneous detection of the clinically important exotoxin potency of isolated S. aureus strains for diagnostic purposes as well as research studies.
Figures
References
-
- Avena R M, Bergdoll M S. Purification and some physicochemical properties of enterotoxin C, Staphylococcus aureus strain 361. Biochemistry. 1967;6:1474–1480. - PubMed
-
- Bergdoll M S, Crass B A, Reiser R F, Robbins R N, Davis J P. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet. 1981;i:1017–1021. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

