Molecular analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and antibiogram of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6B isolates from selected areas within the United States
- PMID: 9705417
- PMCID: PMC105187
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.9.2703-2707.1998
Molecular analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and antibiogram of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6B isolates from selected areas within the United States
Abstract
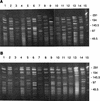
Fifty-eight clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6B, including 16 from Alaska, 14 from Arizona, 11 from Washington, and 17 from seven additional states, were analyzed. The antibiograms of these isolates were assigned to 10 antibiotic profiles based on their susceptibilities to penicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Thirty-two (55%) of these isolates were penicillin nonsusceptible, while 21 (36%) were intermediate or resistant to three or more antibiotics. The restriction endonucleases ApaI and SmaI were used to digest intact chromosomes, and the fragments were resolved by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). The ApaI and SmaI PFGE patterns were combined, and 13 of the 16 Alaskan isolates showed indistinguishable PFGE patterns. One other isolate exhibited highly related ApaI and SmaI PFGE patterns, differing by only one band after restriction with ApaI. Among the 14 isolates from Arizona, 1 was indistinguishable from the predominant ApaI and SmaI PFGE patterns seen in the Alaskan isolates; 5 others were highly related (+/-1 band after cutting with either enzyme) to the Alaskan isolates, suggesting a common ancestral origin. Of the remaining eight isolates, six additional ApaI plus SmaI PFGE patterns were observed. The 28 isolates from the various contiguous states had 22 ApaI plus SmaI PFGE patterns. No correlations were found between specific PFGE patterns, antibiograms, dates of isolation, or geography. The serotype 6B isolates across the contiguous United States were genetically diverse, while the 6B isolates from Alaska appeared to be much less diverse.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of a multidrug-resistant clone of invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 6B in Alaska by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and PspA serotyping.J Infect Dis. 1999 Nov;180(5):1577-83. doi: 10.1086/315062. J Infect Dis. 1999. PMID: 10515818
-
A novel multiresistant Streptococcus pneumoniae serogroup 19 clone from Washington State identified by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and restriction fragment length patterns.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Apr;38(4):1575-80. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.4.1575-1580.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10747146 Free PMC article.
-
Dissemination of a chloramphenicol- and tetracycline-resistant but penicillin-susceptible invasive clone of serotype 5 Streptococcus pneumoniae in Colombia.J Clin Microbiol. 1999 Jul;37(7):2337-42. doi: 10.1128/JCM.37.7.2337-2342.1999. J Clin Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10364609 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae from Toulouse, France.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995 Jun;14(6):491-7. doi: 10.1007/BF02113426. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995. PMID: 7588821
-
Pulsed field gel electrophoresis for molecular epidemiology of penicillin resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae strains.Pathol Biol (Paris). 1994 May;42(5):547-52. Pathol Biol (Paris). 1994. PMID: 7824331
Cited by
-
Application of molecular techniques to the study of hospital infection.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Jul;19(3):512-30. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00025-05. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16847083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular epidemiology of a Shigella flexneri outbreak in a mountainous township in Taiwan, Republic of China.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Mar;39(3):1048-56. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.1048-1056.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11230426 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Vibrio parahaemolyticus O3:K6 from Asia.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000 Sep;66(9):3981-6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.9.3981-3986.2000. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10966418 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 12F isolates associated with rural community outbreaks in Alaska.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 May;51(5):1402-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02880-12. Epub 2013 Feb 13. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23408692 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal carriage of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria in preterm-infants during hospitalization in neonatal intensive care unit (NICU).Pathog Glob Health. 2016 Sep;110(6):238-246. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2016.1229884. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Pathog Glob Health. 2016. PMID: 27650884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appelbaum P C. Antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. An overview. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;15:77–83. - PubMed
-
- Arbeit R D. Laboratory procedures for the epidemiologic analysis of microorganisms. In: Murray P R, Baron E J, Pfaller M A, Tenover F C, Yolken R H, editors. Manual of clinical microbiology. 6th ed. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. pp. 190–208.
-
- Boken D J, Chartrand S A, Moland E S, Goering R V. Colonization with penicillin-nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae in urban and rural child-care centers. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1996;15:667–672. - PubMed
-
- Butler J C, Breiman R F, Lipman H B, Hofmann J, Facklam R R. Serotype distribution of Streptococcus pneumoniae infections among preschool children in the United States, 1978–1994; implications for development of a conjugate vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:885–889. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho C, Geslin P, Vazpato M V. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis in Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated in France and Portugal. Pathol Biol. 1996;44:430–434. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

