Discrimination of Burkholderia gladioli from other Burkholderia species detectable in cystic fibrosis patients by PCR
- PMID: 9705429
- PMCID: PMC105199
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.9.2748-2751.1998
Discrimination of Burkholderia gladioli from other Burkholderia species detectable in cystic fibrosis patients by PCR
Abstract
A procedure for molecular identification of Burkholderia gladioli is described. Specific 16S and 23S rRNA gene signature sequences were defined as primers for PCR. The method allows rapid and specific discrimination of B. gladioli from related species (B. cepacia, B. multivorans, B. vietnamiensis, B. mallei, B. pseudomallei, Ralstonia pickettii, and R. eutropha) and should contribute to the clarification of its role as a human pathogen, e.g., in cystic fibrosis.
Figures

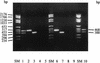
References
-
- Ballard R W, Palleroni N J, Doudoroff M, Stanier RY. Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: Pseudomonas cepacia, P. marginata, P. alliicola, and P. caryophylli. J Gen Microbiol. 1970;60:199–214. - PubMed
-
- Baxter I A, Lambert P A, Simpson I N. Isolation from clinical sources of Burkholderia cepacia possessing characteristics of Burkholderia gladioli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997;39:169–175. - PubMed
-
- Brosius J, Dull T, Noller H F. Gene organisation and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981;148:107–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

