Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Phaeoacremonium inflatipes
- PMID: 9705433
- PMCID: PMC105203
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.9.2763-2765.1998
Phaeohyphomycosis caused by Phaeoacremonium inflatipes
Abstract
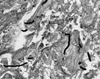
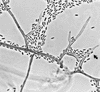
Phaeoacremonium inflatipes, one of three species previously classified as strains of Phialophora parasitica, was identified as the causal agent of a subcutaneous infection of the left foot of an 83-year-old woman from South Carolina. The patient had a granulomatous growth over the anteromedial aspect of her left foot. It was surgically excised, which led to complete healing without complications. Tissue sections of the excised mass stained with hematoxylin and eosin and Gomori's methenamine silver strains showed many septate hyphal elements of various lengths, some exhibiting brownish pigment in the cell walls of the hyphae. Portions of the tissue, when cultured, yielded many colonies which were initially glabrous, off white becoming velvety, greyish brown on aging. Microscopically, their hyphae were septate, branched, and phaeoid and bore lateral and terminal, erect, septate conidiophores. The conidiogenous cells (phialides) were terminal or lateral, mostly monophialidic, subcylindrical to spinelike in shape, and constricted at their bases and bore funnel-shaped, inconspicuous collarettes at their tips. The conidia were subhyaline, oblong, and ellipsoid to allantoid.
Figures
References
-
- Ajello L, Georg L K, Steigbigel R T, Wang C J K. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974;66:490–498. - PubMed
-
- Albernoz M B. Cephalosporium serrae, agente etiologico de micetomas. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1974;54:485–498. - PubMed
-
- Crous P W, Gams W, Wingfield M J, Van Wyk P S. Phaeoacremonium gen. nov. associated with wilt and decline diseases of woody hosts and human infections. Mycologia. 1996;88:786–796.
-
- Fincher R M E, Fisher J F, Padhye A A, Ajello L, Steele J C H., Jr Subcutaneous phaeohyphomycotic abscess caused by Phialophora parasitica. J Med Vet Mycol. 1988;26:311–314. - PubMed
-
- Heath C H, Lendrum J L, Wetherall B L, Wesselingh S L, Gordon D L. Phaeoacremonium parasiticum infective endocarditis following liver transplantation. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25:1251–1252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

