A hypermutable insert in an immunoglobulin transgene contains hotspots of somatic mutation and sequences predicting highly stable structures in the RNA transcript
- PMID: 9705951
- PMCID: PMC2213363
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.188.4.689
A hypermutable insert in an immunoglobulin transgene contains hotspots of somatic mutation and sequences predicting highly stable structures in the RNA transcript
Abstract
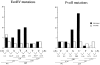
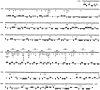
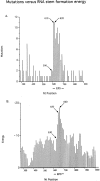
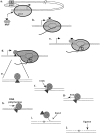
Immunoglobulin (Ig) genes expressed in mature B lymphocytes can undergo somatic hypermutation upon cell interaction with antigen and T cells. The mutation mechanism had previously been shown to depend upon transcription initiation, suggesting that a mutator factor was loaded on an RNA polymerase initiating at the promoter and causing mutations during elongation (Peters, A., and U. Storb. 1996. Immunity. 4:57-65). To further elucidate this process we have created an artificial substrate consisting of alternating EcoRV and PvuII restriction enzyme sites (EPS) located within the variable (V) region of an Ig transgene. This substrate can easily be assayed for the presence of mutations in DNA from transgenic lymphocytes by amplifying the EPS insert and determining by restriction enzyme digestion whether any of the restriction sites have been altered. Surprisingly, the EPS insert was mutated many times more frequently than the flanking Ig sequences. In addition there were striking differences in mutability of the different nucleotides within the restriction sites. The data favor a model of somatic hypermutation where the fine specificity of the mutations is determined by nucleotide sequence preferences of a mutator factor, and where the general site of mutagenesis is determined by the pausing of the RNA polymerase due to secondary structures within the nascent RNA.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Different mismatch repair deficiencies all have the same effects on somatic hypermutation: intact primary mechanism accompanied by secondary modifications.J Exp Med. 1999 Jul 5;190(1):21-30. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.1.21. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10429667 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic hypermutation of an artificial test substrate within an Ig kappa transgene.J Immunol. 1998 Jul 15;161(2):782-90. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9670955
-
Cis-acting sequences that affect somatic hypermutation of Ig genes.Immunol Rev. 1998 Apr;162:153-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01438.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9602361 Review.
-
Strand bias in Ig somatic hypermutation is determined by signal sequence within the variable region.Int Immunol. 2000 Sep;12(9):1245-53. doi: 10.1093/intimm/12.9.1245. Int Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10967019
-
Immunoglobulin transgenes as targets for somatic hypermutation.Int J Dev Biol. 1998;42(7):977-82. Int J Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9853828 Review.
Cited by
-
Generation and repair of AID-initiated DNA lesions in B lymphocytes.Front Med. 2014 Jun;8(2):201-16. doi: 10.1007/s11684-014-0324-4. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Front Med. 2014. PMID: 24748462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of activation-induced deaminase in antibody diversification and genomic instability.Immunol Res. 2013 Mar;55(1-3):287-97. doi: 10.1007/s12026-012-8369-4. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 22956489 Review.
-
Different mismatch repair deficiencies all have the same effects on somatic hypermutation: intact primary mechanism accompanied by secondary modifications.J Exp Med. 1999 Jul 5;190(1):21-30. doi: 10.1084/jem.190.1.21. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10429667 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative regulation of class switch recombination by switch region transcription.J Exp Med. 2001 Aug 6;194(3):365-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.3.365. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11489955 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and the molecular basis of somatic hypermutation of antigen receptor genes.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001 Jan 29;356(1405):67-72. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0750. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2001. PMID: 11205333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kelsoe G. The germinal center reaction. Immunol Today. 1995;16:324–326. - PubMed
-
- MacLennan I. Germinal centers. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;112:117–139. - PubMed
-
- Storb U. The molecular basis of somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:206–214. - PubMed
-
- Betz A, Milstein C, Gonzalez-Fernandes R, Pannell R, Larson T, Neuberger M. Elements regulating somatic hypermutation of an immunoglobulin κ gene: critical role for the intron enhancer/matrix attachment region. Cell. 1994;77:239–248. - PubMed

