High-affinity kainate-type ion channels in rat cerebellar granule cells
- PMID: 9705992
- PMCID: PMC2231062
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.401bk.x
High-affinity kainate-type ion channels in rat cerebellar granule cells
Abstract
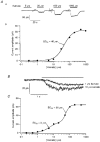
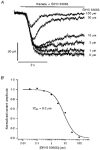
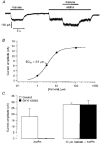
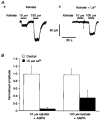
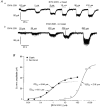
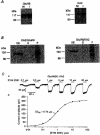
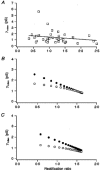
1. Patch-clamp recordings were made from rat cerebellar granule cells in primary culture. In cells pre-exposed to concanavalin A (ConA) to remove kainate receptor desensitization, concentration-response data for kainate showed two components. The EC50 value for the high-affinity component (4 microM) was consistent with activation of kainate-type channels. ConA enhanced the apparent potency of the kainate receptor ligand SYM 2081 by 100-fold. 2. In ConA-treated granule cells, currents evoked by 10 microM kainate were not significantly reduced by the AMPA receptor antagonist GYKI 53655, nor were these currents significantly reduced by the co-application of 100 microM AMPA. Currents activated by low concentrations of kainate in the presence of AMPA were completely inhibited by 10 microM La3+. 3. Single-cell reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis indicated that granule cells express both unedited (Q) and edited (R) versions of GluR5, with the majority of the GluR5 transcripts being unedited. In contrast, BluR6(R) was detected in seven cells and GluR6(Q) was detected in one granule cell. 4. Whole-cell current-voltage curves for kainate-type currents in granule cells were measured and the ratio of the slope conductances at +40 MV and -40 mV was used as an index of rectification. The mean +40 mV/-40 mV ratio determined from thirty-six granule cells was 1.3 +/- 0.1. Spectral density analysis of kainate-evoked whole-cell current noise gave values for the apparent single-channel conductance, gamma(noise), that were on average about 1 pS. 5. To compare further the properties of recombinant kainate channels with the native kainate-type channels in granule cells, we determined EC50 and gamma(noise) values for SYM 2081 in stable cell lines expressing either (GluR6(R) or GluR6(R) and KA2. Co-expression of KA2 with GluR6(R) shifts the EC50 and gamma(noise) values determined for SYM 2081 closer to the values typically found for native kainate-type channels in granule cells. 6. The results demonstrate that cerebellar granule cells in culture express functional kainate-type channels and that in most cells these channels show properties that are similar to those determined for heteromeric channels formed from GluR6(R) and KA2. However, the results also suggest that different granule cells express different repertoires of kainate-type channels with different, and perhaps variable, subunit composition.
Figures




References
-
- Bettler B, Boulter J, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, O'Shea-Greenfield A, Deneris E, Moll C, Borgmeyer U, Hollmann M, Heinemann S. Cloning of a novel glutamate receptor subunit, GluR5: expression in the nervous system during development. Neuron. 1990;5:583–595. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Mülle C. Review: neurotransmitter receptors. II. AMPA and kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34:123–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

