Identification of an ATP-sensitive potassium channel current in rat striatal cholinergic interneurones
- PMID: 9705995
- PMCID: PMC2231058
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.441bk.x
Identification of an ATP-sensitive potassium channel current in rat striatal cholinergic interneurones
Abstract
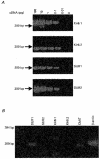
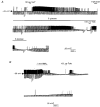
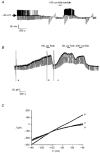
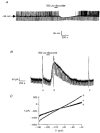
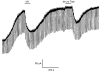
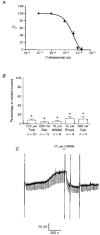
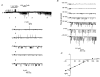
1. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were made from rat striatal cholinergic interneurones in slices of brain tissue in vitro. In the absence of ATP in the electrode solution, these neurones were found to gradually hyperpolarize through the induction of an outward current at -60 mV. This outward current and the resultant hyperpolarization were blocked by the sulphonylureas tolbutamide and glibenclamide and by the photorelease of caged ATP within neurones. 2. This ATP-sensitive outward current was not observed when 2 mM ATP was present in the electrode solution. Under these conditions, 500 microM diazoxide was found to induce an outward current that was blocked by tolbutamide. 3. Using permeabilized patch recordings, neurones were shown to hyperpolarize in response to glucose deprivation or metabolic poisoning with sodium azide (NaN3). The resultant hyperpolarization was blocked by tolbutamide. 4. In cell-attached recordings, metabolic inhibition with 1 mM NaN3 revealed the presence of a tolbutamide-sensitive channel exhibiting a unitary conductance of 44.1 pS. 5. Reverse transcription followed by the polymerase chain reaction using cytoplasm from single cholinergic interneurones demonstrated the expression of the ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel subunits Kir6.1 and SUR1 but not Kir6.2 or SUR2. 6. It is concluded that cholinergic interneurones within the rat striatum exhibit a KATP channel current and that this channel is formed from Kir6.1 and SUR1 subunits.
Figures

References
-
- Chesselet M-F, Gonzales C, Lin C-S, Polsky K, Jin B-K. Ischemic damage in the striatum of adult gerbils: Relative sparing of somatostatinergic and cholinergic interneurons contrasts with loss of efferent neurons. Experimental Neurology. 1990;110:209–218. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

