Activation of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors by sympathetic nerve stimulation in the large intestine of the rat
- PMID: 9706003
- PMCID: PMC2231039
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.549bk.x
Activation of alpha- and beta-adrenoceptors by sympathetic nerve stimulation in the large intestine of the rat
Abstract
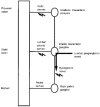
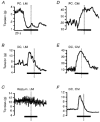
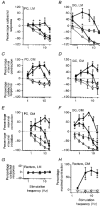
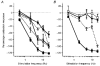
1. The effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation on the motility of the circular and longitudinal muscle of the large intestine were investigated in vitro, and the involvement of various adrenoceptor subtypes determined. A comparison between the sympathetic supply arising from the prevertebral and pelvic ganglia was also made. 2. In the longitudinal muscle of the distal colon, sympathetic nerve stimulation caused responses which were contractile (0.1-2 Hz), biphasic (5-10 Hz) or purely inhibitory (20-30 Hz). All contractile responses were removed with phentolamine (3 microM), whereas the inhibitory responses were significantly diminished by propranolol (0.1 microM) and completely abolished by alprenolol (3 microM) or nadolol (300 microM). 3. In the longitudinal muscle of the proximal colon, the effects of sympathetic nerve stimulation were predominantly inhibitory. Some of this inhibition was removed by propranolol (0.1 microM), but was largely unaffected by alprenolol (3 microM). The remainder of the inhibitory response was probably non-noradrenergic as it was not removed by a combination of phentolamine (3 microM) and alprenolol (3 microM). 4. In the circular muscle of both the proximal and distal colon, sympathetic stimulation caused a strong contractile response which was completely removed by phentolamine (3 microM) to reveal an inhibitory response. This inhibitory response was unchanged by propranolol (0.1 microM) but was removed by alprenolol (3 microM), following which a weak non-noradrenergic contractile response was unmasked. 5. Stimulation of the hypogastric nerve to activate pelvic sympathetic pathways had no effect on the motility of the longitudinal muscle, but caused a contractile response in the circular muscle which was completely removed by phentolamine (3 microM). 6. We conclude that sympathetic nerves innervate adrenoceptors of different types in the various muscle layers and regions of the colon. They innervate a mixture of alpha-, and beta(3)-adrenoceptors in the longitudinal muscle of the proximal colon, alpha-, classical beta- and beta(3)-adrenoceptors in the distal colon, and primarily alpha-adrenoceptors with a few beta(3)-adrenoceptors in the circular muscle. In addition, the pelvic sympathetic innervation of the rectum differs from the prevertebral supply by innervating only excitatory alpha-adrenoceptors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stimulation of lumbar sympathetic nerves evokes contractions of cat colon circular muscle mediated by ATP and noradrenaline.Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov;110(3):1260-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13951.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1993. PMID: 7905343 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a noradrenergic innervation to "atypical" beta adrenoceptors (or putative beta-3 adrenoceptors) in the ileum of guinea pig.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):192-200. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992. PMID: 1346160
-
Vasoconstrictor responses of rat tail artery to sympathetic nerve stimulation contain a component due to activation of postjunctional beta- or alpha 2-adrenoceptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 20;177(1-2):35-41. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90547-j. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990. PMID: 1971218
-
The role of adrenoceptors in circulatory and metabolic regulation.Am Heart J. 1988 Nov;116(5 Pt 2):1384-92. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(88)90128-7. Am Heart J. 1988. PMID: 2903648 Review.
-
Adrenoceptors in airway smooth muscle.Pharmacol Ther. 1990;48(3):295-322. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(90)90051-3. Pharmacol Ther. 1990. PMID: 1982179 Review.
Cited by
-
Sympathetic inhibition of ascending and descending interneurones during the peristaltic reflex in the isolated guinea-pig distal colon.J Physiol. 1999 Sep 1;519 Pt 2(Pt 2):539-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0539m.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10457069 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbiota Regulates the Sympathetic Nerve Activity and Peripheral Serotonin Through Hypothalamic MicroRNA-204 in Order to Increase the Browning of White Adipose Tissue in Obesity.Cureus. 2022 Feb 4;14(2):e21913. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21913. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35155042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Altered Signaling on EFS-Induced Colon Contractility in Diabetic Rats.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020 Jul 1;28(4):328-336. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.181. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32126734 Free PMC article.
-
Differential adrenergic response to extrinsic denervation in canine longitudinal jejunal and ileal smooth muscle.J Gastrointest Surg. 2002 May-Jun;6(3):418-25. doi: 10.1016/s1091-255x(02)00006-9. J Gastrointest Surg. 2002. PMID: 12022995
-
The signaling of amitriptyline-induced inhibitory effect on electrical field stimulation response in colon smooth muscle.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016 Sep;389(9):961-70. doi: 10.1007/s00210-016-1259-x. Epub 2016 May 28. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27234925
References
-
- Arch JRS, Kaumann AJ. β3 and atypical β-adrenoceptors. Medical Research Reviews. 1993;13:663–729. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Jänig W. Afferent and sympathetic neurons projecting into lumbar visceral nerves of the male rat. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1991;314:429–436. - PubMed
-
- Baron R, Jänig W, McLachlan EM. The afferent and sympathetic components of the lumbar spinal outflow to the colon and pelvic organs in the cat. I. The hypogastric nerve. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1985;238:135–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

