Slow recovery of impaired phrenic responses to hypoxia following perinatal hyperoxia in rats
- PMID: 9706034
- PMCID: PMC2231139
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.599bh.x
Slow recovery of impaired phrenic responses to hypoxia following perinatal hyperoxia in rats
Abstract
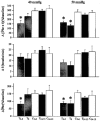
1. Previous studies demonstrated that both ventilatory and phrenic nerve responses to acute hypoxia are greatly attenuated in adult rats (3-5 months old) previously exposed to 1 month of perinatal hyperoxia (60 % O2; perinatal treated rats). The present study tested the hypothesis that this functional impairment recovers spontaneously with advancing age in perinatal treated rats. 2. Hypoxia-induced chemoreflexes were examined by measuring integrated phrenic responses to strictly controlled isocapnic hypoxia in urethane-anaesthetized, vagotomized, paralysed and ventilated rats at different ages. 3. At 50 mmHg Pa,O2 (arterial O2 partial pressure), the hypoxia-induced increase in minute phrenic activity was significantly attenuated in both 3- to 5-month-old (166 +/- 15% of baseline) and 6-month-old (130 +/- 17%) perinatal treated rats, relative to 3- to 6-month-old, untreated control rats (279 +/- 28%; both P < 0.05). However, at 40 mmHg Pa,O2, the hypoxic minute phrenic activity response was attenuated only in 3- to 5-month-old (154 +/- 33%), but not 6-month-old (232 +/- 33%) perinatal treated rats versus control rats (293 +/- 30%). 4. The minute phrenic activity response to hypoxia was not significantly different between geriatric perinatal treated rats (14-15 months) and untreated geriatric control rats at either 50 mmHg (treated: 250 +/- 20% versus control: 274 +/- 23%) or 40 mmHg Pa,O2 (treated: 292 +/- 19% versus control: 315 +/- 36%). 5. These data suggest that partial spontaneous recovery may occur in 6-month-old perinatal treated rats and that full recovery occurs by 15 months of age.
Figures
References
-
- Fukuda Y. Changes in ventilatory response to hypoxia in the rat during growth and aging. Pflügers Archiv. 1992;421:200–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

