Biochemical basis of SOS-induced mutagenesis in Escherichia coli: reconstitution of in vitro lesion bypass dependent on the UmuD'2C mutagenic complex and RecA protein
- PMID: 9707548
- PMCID: PMC21409
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9755
Biochemical basis of SOS-induced mutagenesis in Escherichia coli: reconstitution of in vitro lesion bypass dependent on the UmuD'2C mutagenic complex and RecA protein
Abstract
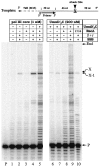
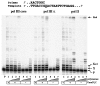
Damage-induced SOS mutagenesis requiring the UmuD'C proteins occurs as part of the cells' global response to DNA damage. In vitro studies on the biochemical basis of SOS mutagenesis have been hampered by difficulties in obtaining biologically active UmuC protein, which, when overproduced, is insoluble in aqueous solution. We have circumvented this problem by purifying the UmuD'2C complex in soluble form and have used it to reconstitute an SOS lesion bypass system in vitro. Stimulated bypass of a site-directed model abasic lesion occurs in the presence of UmuD'2C, activated RecA protein (RecA*), beta-sliding clamp, gamma-clamp loading complex, single-stranded binding protein (SSB), and either DNA polymerases III or II. Synthesis in the presence of UmuD'2C is nonprocessive on damaged and undamaged DNA. No lesion bypass is observed when wild-type RecA is replaced with RecA1730, a mutant that is specifically defective for Umu-dependent mutagenesis. Perhaps the most noteworthy property of UmuD'2C resides in its ability to stimulate both nucleotide misincorporation and mismatch extension at aberrant and normal template sites. These observations provide a biochemical basis for the role of the Umu complex in SOS-targeted and SOS-untargeted mutagenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Friedberg E C, Walker G C, Siede W. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1995.
-
- Echols H, Goodman M F. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:477–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

