The Candida albicans KRE9 gene is required for cell wall beta-1, 6-glucan synthesis and is essential for growth on glucose
- PMID: 9707560
- PMCID: PMC21421
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9825
The Candida albicans KRE9 gene is required for cell wall beta-1, 6-glucan synthesis and is essential for growth on glucose
Abstract
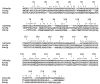
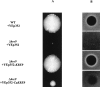
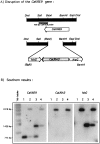
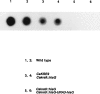
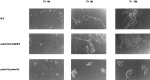
We have isolated CaKRE9, a gene from Candida albicans, that is a functional homologue of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae KRE9 gene involved in beta-1,6-glucan synthesis. Disruption of the CaKRE9 gene in C. albicans shows that CaKre9p is required for the synthesis or assembly of this fungal polymer. Homozygous null disruptants of CaKRE9 grow poorly on galactose and fail to form hyphae in serum, and, in growth medium containing glucose, the gene is essential. Thus, the CaKRE9 gene product is a potentially useful candidate as a target for fungal-specific drugs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolation of the Candida albicans homologs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae KRE6 and SKN1: expression and physiological function.J Bacteriol. 1997 Apr;179(7):2363-72. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.7.2363-2372.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9079924 Free PMC article.
-
The KNH1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a functional homolog of KRE9.Yeast. 1996 Jun 15;12(7):683-92. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19960615)12:7%3C683::AID-YEA959%3E3.0.CO;2-8. Yeast. 1996. PMID: 8810042
-
Isolation of Candida glabrata homologs of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae KRE9 and KNH1 genes and their involvement in cell wall beta-1,6-glucan synthesis.J Bacteriol. 1998 Oct;180(19):5020-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.180.19.5020-5029.1998. J Bacteriol. 1998. PMID: 9748432 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal beta(1,3)-D-glucan synthesis.Med Mycol. 2001;39 Suppl 1:55-66. doi: 10.1080/mmy.39.1.55.66. Med Mycol. 2001. PMID: 11800269 Review.
-
beta-1,6-Glucan synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Microbiol. 2000 Feb;35(3):477-89. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01713.x. Mol Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10672173 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular analysis of the Candida albicans homolog of Saccharomyces cerevisiae MNN9, required for glycosylation of cell wall mannoproteins.J Bacteriol. 1999 Dec;181(24):7439-48. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.24.7439-7448.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10601199 Free PMC article.
-
Stress responsive glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein SsGSP1 contributes to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum virulence.Virulence. 2025 Dec;16(1):2503434. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2503434. Epub 2025 May 18. Virulence. 2025. PMID: 40353429 Free PMC article.
-
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome-wide mutant screen for altered sensitivity to K1 killer toxin.Genetics. 2003 Mar;163(3):875-94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/163.3.875. Genetics. 2003. PMID: 12663529 Free PMC article.
-
KRE5 gene null mutant strains of Candida albicans are avirulent and have altered cell wall composition and hypha formation properties.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Dec;3(6):1423-32. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.6.1423-1432.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15590817 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale identification of putative exported proteins in Candida albicans by genetic selection.Eukaryot Cell. 2002 Aug;1(4):514-25. doi: 10.1128/EC.1.4.514-525.2002. Eukaryot Cell. 2002. PMID: 12456000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pfaller, M. A. (1995) J. Hosp. Infect. 30, Suppl., 329–338. - PubMed
-
- Pfaller, M. A. (1996) Clin. Infect. Dis. 22, Suppl. 2, S89–S94. - PubMed
-
- Odds F C. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 1996;6:141–144. - PubMed
-
- Wingard J R. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:115–125. - PubMed
-
- Goffeau A, Barrell B G, Bussey H, Davis R W, Dujon B, Feldmann H, Galibert F, Hoheisel J D, Jacq C, Johnston M, et al. Science. 1996;274:546–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

