A 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis
- PMID: 9707569
- PMCID: PMC21430
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9879
A 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase catalyzing the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate in an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for terpenoid biosynthesis
Abstract
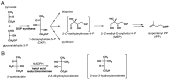
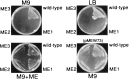
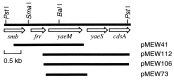
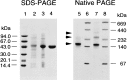
Several eubacteria including Esherichia coli use an alternative nonmevalonate pathway for the biosynthesis of isopentenyl diphosphate instead of the ubiquitous mevalonate pathway. In the alternative pathway, 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol or its 4-phosphate, which is proposed to be formed from 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate via intramolecular rearrangement followed by reduction process, is one of the biosynthetic precursors of isopentenyl diphosphate. To clone the gene(s) responsible for synthesis of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate, we prepared and selected E. coli mutants with an obligatory requirement for 2-C-methylerythritol for growth and survival. All the DNA fragments that complemented the defect in synthesizing 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate of these mutants contained the yaeM gene, which is located at 4.2 min on the chromosomal map of E. coli. The gene product showed significant homologies to hypothetical proteins with unknown functions present in Haemophilus influenzae, Synechocystis sp. PCC6803, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Helicobacter pyroli, and Bacillus subtilis. The purified recombinant yaeM gene product was overexpressed in E. coli and found to catalyze the formation of 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate from 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate in the presence of NADPH. Replacement of NADPH with NADH decreased the reaction rate to about 1% of the original rate. The enzyme required Mn2+, Co2+, or Mg2+ as well. These data clearly show that the yaeM gene encodes an enzyme, designated 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase, that synthesizes 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate from 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate, in a single step by intramolecular rearrangement and reduction and that this gene is responsible for terpenoid biosynthesis in E. coli.
Figures

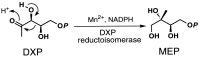
References
-
- Sacchettini J C, Poulter C D. Science. 1997;277:1788–1789. - PubMed
-
- Rohmer M, Seeman M, Horbach S, Bringer-Meyer S, Sahm H. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:2564–2566.
-
- Seto H, Watanabe H, Furihata K. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996;37:7979–7982.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

