Morphine-activated opioid receptors elude desensitization by beta-arrestin
- PMID: 9707575
- PMCID: PMC21436
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.9914
Morphine-activated opioid receptors elude desensitization by beta-arrestin
Abstract
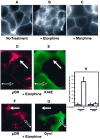
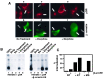
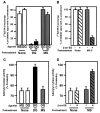
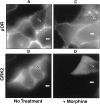
mu opioid receptors are targets of native opioid peptides and addictive analgesic drugs. A major clinical liability of opiate drugs is their ability to cause physiological tolerance. Individual opiates, such as morphine and etorphine, differ both in their ability to promote physiological tolerance and in their effects on receptor regulation by endocytosis. Here, we demonstrate that arrestins play a fundamental role in mediating this agonist-selective regulation and that morphine-activated mu receptors fail to undergo arrestin-dependent uncoupling from cognate G proteins. Thus, highly addictive opiate drugs elude a fundamental mode of physiological regulation that is mediated by agonist-specific interaction of opioid receptors with arrestins.
Figures
References
-
- Evans C J. In: Diversity Among the Opioid Receptors. Korenman S G, Barchas J D, editors. New York: Oxford University Press; 1993. pp. 31–48.
-
- Grudt T J, Williams J T. Rev Neurosci. 1995;6:279–286. - PubMed
-
- Matthes H W, Maldonado R, Simonin F, Valverde O, Slowe S, Kitchen I, Befort K, Dierich A, Le M M, Dolle P, et al. Nature (London) 1996;383:819–823. - PubMed
-
- Yu Y, Zhang L, Yin X, Sun H, Uhl G R, Wang J B. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:28869–28874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

