Small intestinal T cells of celiac disease patients recognize a natural pepsin fragment of gliadin
- PMID: 9707598
- PMCID: PMC21459
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.10050
Small intestinal T cells of celiac disease patients recognize a natural pepsin fragment of gliadin
Abstract
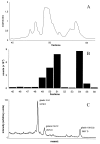
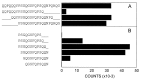
Celiac disease is a common severe intestinal disease resulting from intolerance to dietary wheat gluten and related proteins. The large majority of patients expresses the HLA-DQ2 and/or DQ8 molecules, and gluten-specific HLA-DQ-restricted T cells have been found at the site of the lesion in the gut. The nature of peptides that are recognized by such T cells, however, has been unclear so far. We now report the identification of a gliadin-derived epitope that dominantly is recognized by intestinal gluten-specific HLA-DQ8-restricted T cells. The characterization of such epitopes is a key step toward the development of strategies to interfere in mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of celiac disease.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

