T cells recognizing leukemic CD34(+) progenitor cells mediate the antileukemic effect of donor lymphocyte infusions for relapsed chronic myeloid leukemia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 9707616
- PMCID: PMC21477
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.17.10152
T cells recognizing leukemic CD34(+) progenitor cells mediate the antileukemic effect of donor lymphocyte infusions for relapsed chronic myeloid leukemia after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Abstract
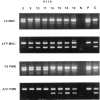
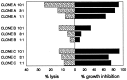
Adoptive immunotherapy with donor lymphocyte infusions (DLI) is an effective treatment for relapsed chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. To identify the effector and target cell populations responsible for the elimination of the leukemic cells in vivo we developed an assay to measure the frequency of T lymphocyte precursor cells capable of suppressing leukemic progenitor cells. Target cells in this assay were CML cells that were cultured in the presence of stem cell factor, interleukin 3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and erythropoietin. [3H]thymidine incorporation at day 7 represented the proliferation of the progeny of the CD34(+) CML progenitor cells, and not of the more mature CD34(-) CML cells. Effector cells were mononuclear cells, which were used in a limiting dilution analysis to measure the frequencies of CML progenitor cell-inhibitory lymphocyte precursors (PCILp) in peripheral blood of seven patients before and after DLI for relapsed CML. In the six patients who entered complete remission, a 5- to 100-fold increase of PCILp was found during the clinical response. In the patient with resistant relapse the frequency of PCILp was <10 per ml before and after DLI. Leukemia-reactive helper T lymphocyte precursor frequencies remained unchanged after DLI. A significant increase in cytotoxic T lymphocyte precursor frequency against more mature leukemic cells was found in only two responding patients. These results indicate that T cells specifically directed against CD34(+) CML progenitor cells mediate the antileukemic effect of DLI.
Figures



References
-
- Falkenburg J H F, Smit W M, Willemze R. Immunol Rev. 1997;157:223–230. - PubMed
-
- Weiden P L, Flournoy N, Thomas E D, Prentice R, Fefer A, Buckner C D, Storb R. N Engl J Med. 1979;300:1068–1073. - PubMed
-
- Gale R P, Horowitz M M, Ash R C, Champlin R E, Goldman J M, Rimm A A, Ringden O, Stone J A V, Bortin M M. Ann Intern Med. 1994;120:646–652. - PubMed
-
- Apperley J F, Jones L, Hale G, Waldmann H, Hows J, Rombos Y, Tsatalas C, Marcus R E, Goolden A W, Gordon Smith E C, et al. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1986;1:53–66. - PubMed
-
- Goldman J M, Gale R P, Horowitz M M, Bigs J C, Champlin R E, Gluckman E, Hoffmann R G, Jacobsen S J, Marmont A M, McGlave P B, et al. Ann Int Med. 1988;108:806–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

