High expression of stanniocalcin in differentiated brain neurons
- PMID: 9708804
- PMCID: PMC1852984
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65587-3
High expression of stanniocalcin in differentiated brain neurons
Abstract
Stanniocalcin (STC) is a glycoprotein hormone first found in fish, in which it regulates calcium homeostasis and protects against hypercalcemia. Human and mouse stc cDNA were recently cloned. We found a dramatically upregulated expression of STC during induced neural differentiation in a human neural crest-derived cell line, Paju. Immunohistochemical staining of sections from human and adult mouse brain revealed abundant presence of STC in the neurons with no activity in the glial cells. STC expression was not seen in immature brain neurons of fetal or newborn mice. Given that STC has been found to regulate calcium/phosphate metabolism in some mammalian epithelia, we suggest that STC may act as a regulator of calcium homeostasis in terminally differentiated brain neurons.
Figures


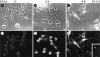
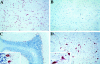
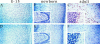
References
-
- Stannius H: Uber nebenniere bei knochenfischen. Arch Anat Physiol 1839, 6:97-101
-
- Wagner GF, Gellersen B, Friesen HG: Primary culture of teleocalcin cells from rainbow trout corpuscles of Stannius: regulation of teleocalcin secretion by calcium. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1989, 62:31-39 - PubMed
-
- Wagner GF, Milliken C, Friesen HG, Copp DH: Studies on the regulation and characterization of plasma stanniocalcin in rainbow trout. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1991, 79:129-138 - PubMed
-
- Fenwick JC, So YP: A perfusion study of the effect of stanniectomy on the net influx of calcium 45 across an isolated eel gill (1). J Exp Zool 1974, 188:125-131 - PubMed
-
- Lafeber FP, Flik G, Wendelaar Bonga SE, Perry SF: Hypocalcin from Stannius corpuscles inhibits gill calcium uptake in trout. Am J Physiol 1988, 254:891-896 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

