Extrahepatic expression and regulation of protein C in the mouse
- PMID: 9708814
- PMCID: PMC1852986
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65597-6
Extrahepatic expression and regulation of protein C in the mouse
Abstract
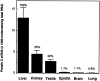
Activated protein C (APC) acts as an anticoagulant by inhibiting coagulation factors Va and VIIIa. Although the liver appears to be the primary site of protein C (PC) synthesis, the demonstration that other components of this system are produced extrahepatically raises the possibility that PC itself is synthesized in other tissues. We therefore used quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, in situ hybridization, and immunohistochemistry to screen various murine tissues for PC expression. Relatively high levels of PC mRNA were detected in the kidney (35% of liver) and testis (22% of liver). PC mRNA and antigen were demonstrated in tubular epithelial cells in the renal cortex, in spermatogenic cells in the testis, and in epithelial cells in the epididymis. Low but significant levels of PC mRNA were detected in the epididymis (1.7% of the level in liver), brain (1.1% of liver), and lung (0.8% of liver). PC antigen was demonstrated in bronchial epithelial cells in the lung, in pyramidal neurons in the cerebrum, and in Purkinje cells in the cerebellum. The extrahepatic expression of PC mRNA (ie, in the kidney) was significantly decreased in mice with renal disease (eg, in MRL lpr/lpr mice with autoimmune lupus nephritis, in db/db mice with diabetic nephropathy, and in endotoxin-treated mice with acute renal injury). The decreased renal expression of PC may contribute to the increased procoagulant potential of the kidney during septic and inflammatory processes and to the progression of kidney disease associated with these conditions.
Figures




References
-
- Esmon CT: The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem 1989, 264:4743-4746 - PubMed
-
- Marlar RA, Kleiss AJ, Griffin JH: Mechanism of action of human activated protein C, a thrombin-dependent anticoagulant enzyme. Blood 1982, 59:1067-1072 - PubMed
-
- Bajzar L, Manuel R, Nesheim ME: Purification and characterization of TAFI, a thrombin-activable fibrinolysis inhibitor. J Biol Chem 1995, 270:14477-14484 - PubMed
-
- van Hinsbergh VWM, Bertina RM, van Wijngaarden A, van Tilburg NH, Emeis JJ, Haverkate F: Activated protein C decreases plasminogen activator-inhibitor activity in endothelial cell-conditioned medium. Blood 1985, 65:444-451 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

