Hepatocellular hyperplasia, plasmacytoma formation, and extramedullary hematopoiesis in interleukin (IL)-6/soluble IL-6 receptor double-transgenic mice
- PMID: 9708822
- PMCID: PMC1852966
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65605-2
Hepatocellular hyperplasia, plasmacytoma formation, and extramedullary hematopoiesis in interleukin (IL)-6/soluble IL-6 receptor double-transgenic mice
Abstract
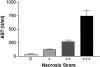
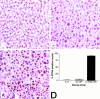
Cytokines interact not only with membrane anchored receptors, but also with specific soluble receptors which circulate in the bloodstream. In general, soluble cytokine receptors such as soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor, soluble interleukin 1 receptor, and soluble interleukin 4 receptor compete with their membrane-bound counterparts for the ligands and therefore act as antagonists. In contrast, soluble receptors for cytokines of the interleukin-6 (IL-6) family complex with their ligands act agonistically. Interestingly, the complex of IL-6 and the soluble interleukin 6 receptor (sIL-6R) activates target cells that do not express the membrane-bound IL-6R and therefore cannot respond to IL-6. To identify cellular responses that are due to IL-6/sIL-6R but not to IL-6 alone, IL-6/sIL-6R double-transgenic mice were generated and compared with IL-6 single-transgenic mice. IL-6/sIL-6R transgenic mice develop a severe phenotype showing 1) marked hepatocellular hyperplasia frequently surrounded by peliosis and necrosis, 2) significant acceleration and aggravation of plasmacytoma formation, and 3) excessive activation of extramedullary hematopoiesis in spleen and liver followed by a subsequent increase of all cellular components in the peripheral blood. These in vivo data suggest that the sIL-6R recruits primarily unresponsive cell populations such as hematopoietic progenitor cells and hepatocytes to IL-6-induced proliferation, but also enhances the known mitogenic effect of IL-6 on plasma cells and thereby contributes to plasmacytoma formation.
Figures
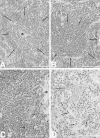
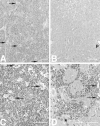
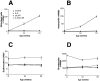
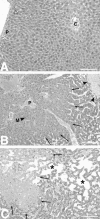

References
-
- Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T: Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol 1993, 54:1-78 - PubMed
-
- Bauer J, Herrmann F: Interleukin-6 in clinical medicine. Ann Hematol 1991, 62:203-210 - PubMed
-
- Gauldie J, Richards C, Harnish D, Lansdorp P, Baumann H: Interferon beta 2/B-cell stimulatory factor type 2 shares identity with monocyte-derived hepatocyte-stimulating factor and regulates the major acute phase protein response in liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987, 84:7251-7255 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grötzinger J, Kurapkat G, Wollmer A, Kalai M, Rose-John S: The family of the IL-6-type cytokines: specificity and promiscuity of the receptor complexes. Proteins Struct Funct Genet 1997, 27:96-109 - PubMed
-
- Hibi M, Nakajima K, Hirano T: IL-6 cytokine family and signal transduction: a model of the cytokine system. J Mol Med 1996, 74:1-12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

