Targeted recruitment of the Sin3-Rpd3 histone deacetylase complex generates a highly localized domain of repressed chromatin in vivo
- PMID: 9710596
- PMCID: PMC109097
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.9.5121
Targeted recruitment of the Sin3-Rpd3 histone deacetylase complex generates a highly localized domain of repressed chromatin in vivo
Abstract
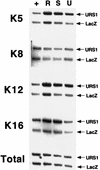
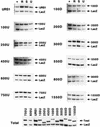
Eukaryotic organisms contain a multiprotein complex that includes Rpd3 histone deacetylase and the Sin3 corepressor. The Sin3-Rpd3 complex is recruited to promoters by specific DNA-binding proteins, whereupon it represses transcription. By directly analyzing the chromatin structure of a repressed promoter in yeast cells, we demonstrate that transcriptional repression is associated with localized histone deacetylation. Specifically, we observe decreased acetylation of histones H3 and H4 (preferentially lysines 5 and 12) that depends on the DNA-binding repressor (Ume6), Sin3, and Rpd3. Mapping experiments indicate that the domain of histone deacetylation is highly localized, occurring over a range of one to two nucleosomes. Taken together with previous observations, these results define a novel mechanism of transcriptional repression which involves targeted recruitment of a histone-modifying activity and localized perturbation of chromatin structure.
Figures
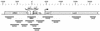


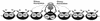
References
-
- Alland L, Muhle R, Hou H, Potes J, Chin L, Schreiber-Agus N, DePinho R A. Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 1997;387:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio O M, Weinstein D M, Bell S P. Components and dynamics of DNA replication complexes in S. cerevisiae: redistribution of MCM proteins and Cdc45p during S phase. Cell. 1997;91:59–69. - PubMed
-
- Bannister A J, Kouzarides T. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature. 1996;384:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Braunstein M, Rose A B, Holmes S G, Allis C D, Broach J R. Transcriptional silencing in yeast is associated with reduced nucleosome acetylation. Genes Dev. 1993;7:592–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
