Calcium-evoked dendritic exocytosis in cultured hippocampal neurons. Part II: mediation by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
- PMID: 9712652
- PMCID: PMC6792974
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-17-06814.1998
Calcium-evoked dendritic exocytosis in cultured hippocampal neurons. Part II: mediation by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II
Abstract
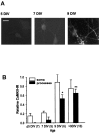
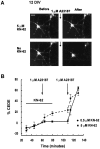
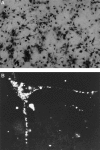
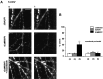
Calcium-evoked dendritic exocytosis (CEDE), demonstrated in cultured hippocampal neurons, is a novel mechanism that could play a role in synaptic plasticity. A number of forms of neuronal plasticity are thought to be mediated by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII). Here, we investigate the role of CaMKII in CEDE. We find that the developmental time course of CEDE parallels the expression of alphaCaMKII, a dominant subunit of CaMKII. An inhibitor of this enzyme, KN-62, blocks CEDE. Furthermore, 7 d in vitro neurons (which normally do not express alphaCaMKII nor show CEDE) can undergo CEDE when infected with a recombinant virus producing alphaCaMKII. Expression of a constitutively active CaMKII produces dendritic exocytosis in the absence of calcium stimulus, and this exocytosis is blocked by nocodazole, an inhibitor of microtubule polymerization that also blocks CEDE. These results indicate that CEDE is mediated by the activation of CaMKII, consistent with the view that CEDE plays a role in synaptic plasticity.
Figures

References
-
- Banker GA, Goslin K. Culturing nerve cells. MIT; Cambridge, MA: 1990.
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science. 1997;276:2042–2045. - PubMed
-
- Baude A, Nusser Z, Molnar E, McIlhinney RA, Somogyi P. High-resolution immunogold localization of AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunits at synaptic and non-synaptic sites in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 1995;69:1031–1055. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MK, Erondu NE, Kennedy MB. Purification and characterization of a calmodulin-dependent protein kinase that is highly concentrated in brain. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:12735–12744. - PubMed
-
- Braun AP, Schulman H. The multifunctional calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: from form to function. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:417–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
