N-cadherin redistribution during synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 9712659
- PMCID: PMC6792987
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-17-06892.1998
N-cadherin redistribution during synaptogenesis in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
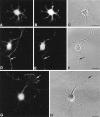
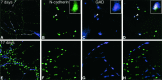
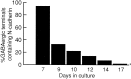
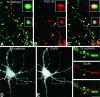
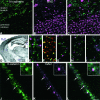
Cadherins are homophilic adhesion molecules that, together with their intracellular binding partners the catenins, mediate adhesion and signaling at a variety of intercellular junctions. This study shows that neural (N)-cadherin and beta-catenin, an intracellular binding partner for the classic cadherins, are present in axons and dendrites before synapse formation and then cluster at developing synapses between hippocampal neurons. N-cadherin is expressed initially at all synaptic sites but rapidly becomes restricted to a subpopulation of excitatory synaptic sites. Sites of GABAergic, inhibitory synapses in mature cultures therefore lack N-cadherin but are associated with clusters of beta-catenin, implying that they contain a different classic cadherin. These findings indicate that N-cadherin adhesion may stabilize early synapses that can then be remodeled to express a different cadherin and that cadherins systematically differentiate between functionally (excitatory and inhibitory) and spatially distinct synaptic sites on single neurons. These results suggest that differential cadherin expression may orchestrate the point-to-point specificity displayed by developing synapses.
Figures



References
-
- Arndt K, Redies C. Restricted expression of R-cadherin by brain nuclei and neural circuits of the developing chicken brain. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373:373–399. - PubMed
-
- Arndt K, Nakagawa S, Takeichi M, Redies C. Cadherin-defined segments and parasagittal cell ribbons in the developing chicken cerebellum. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998;10:211–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
