The biphasic mRNA expression pattern of bovine interleukin-8 in Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide-stimulated alveolar macrophages is primarily due to tumor necrosis factor alpha
- PMID: 9712752
- PMCID: PMC108490
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4087-4092.1998
The biphasic mRNA expression pattern of bovine interleukin-8 in Pasteurella haemolytica lipopolysaccharide-stimulated alveolar macrophages is primarily due to tumor necrosis factor alpha
Abstract
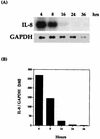
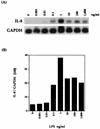
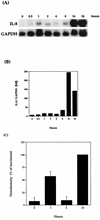
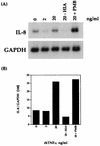
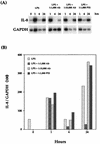
Pasteurella haemolytica serotype 1 is the bacterial agent responsible for the pathophysiological events associated with bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis. Our previous studies support a role for the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from P. haemolytica in the induction of proinflammatory cytokines. One of the pathological hallmarks of bovine pneumonic pasteurellosis is an influx of neutrophils into the alveolar spaces. This pronounced influx suggests the local production of a chemotactic factor(s) such as interleukin-8 (IL-8). In the context of the lung, the alveolar macrophage appears to be the major producer of IL-8, a proinflammatory cytokine with potent neutrophil chemotactic activity. By using Northern blot analysis, we have examined the kinetics of IL-8 mRNA expression in P. haemolytica LPS-stimulated bovine alveolar macrophages and found that 1 ng of LPS per ml induces maximal expression of IL-8 mRNA. The results also indicate a biphasic time course expression pattern in which IL-8 mRNA levels peak between 1 and 2 h in the first phase and between 16 and 24 h in the second phase (P < 0.01). In addition, monospecific polyclonal antibodies were used to demonstrate the role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in the second phase of IL-8 mRNA expression. Our findings support a role for P. haemolytica LPS and TNF-alpha in the induction of IL-8 from bovine alveolar macrophages.
Figures



References
-
- Babiuk L A, Lawman M J P, Biol M I, Gifford G A. A seminar in bovine immunology. Western Veterinary Conference. Las Vegas, Nev: Veterinary Learning Systems Co., Inc.; 1987. Bovine respiratory disease: pathogenesis and control by interferon; pp. 12–24.
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
-
- Confer A W, Panciera R J, Clinkenbeard K D, Mosier D A. Molecular aspects of virulence of Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Vet Res. 1990;54:S48–S52. - PubMed
-
- DeForge L E, Kenney J S, Jones M L, Warren J S, Remick D G. Biphasic production of IL-8 in lipolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human whole blood. J Immunol. 1992;148:2133–2141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

