Low endotoxic potential of Legionella pneumophila lipopolysaccharide due to failure of interaction with the monocyte lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14
- PMID: 9712761
- PMCID: PMC108499
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4151-4157.1998
Low endotoxic potential of Legionella pneumophila lipopolysaccharide due to failure of interaction with the monocyte lipopolysaccharide receptor CD14
Abstract
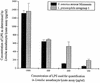
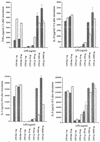
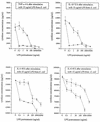
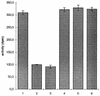
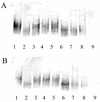
Legionella pneumophila, a gram-negative bacterium causing Legionnaires' disease and Pontiac fever, was shown to be highly reactive in in vitro gelation of Limulus lysate but not able to induce fever and the local Shwartzman reaction in rabbits and mice. We analyzed the capacity of purified L. pneumophila lipopolysaccharide (LPS-Lp) to induce activation of the human monocytic cell line Mono Mac 6, as revealed by secretion of proinflammatory cytokines and desensitization to subsequent LPS stimulation. We showed that despite normal reactivity of LPS-Lp in the Limulus amoebocyte lysate assay, induction of cytokine secretion in Mono Mac 6 cells and desensitization to an endotoxin challenge required LPS-Lp concentrations 1,000 times higher than for LPS of Salmonella enterica serovar Minnesota. Therefore, we examined the interaction of LPS-Lp with the LPS receptor CD14. We demonstrated that LPS-Lp did not bind to membrane-bound CD14 expressed on transfected CHO cells, nor did it react with soluble CD14. Our results suggest that the low endotoxic potential of LPS-Lp is due to a failure of interaction with the LPS receptor CD14.
Figures
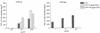
References
-
- Blondiau C, Lagadec P, Lejeune P, Onier N, Cavaillon J M, Jeannin J F. Correlation between the capacity to activate macrophages in vitro and the antitumor activity in vivo of lipopolysaccharides from different bacterial species. Immunobiology. 1994;190:243–254. - PubMed
-
- Fumarola D. Attempts to biological demonstration of endotoxin potency in Legionella pneumophila. Ann Sclavo. 1979;21:258–263. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

