Deletion of repeats in the alpha C protein enhances the pathogenicity of group B streptococci in immune mice
- PMID: 9712787
- PMCID: PMC108525
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4347-4354.1998
Deletion of repeats in the alpha C protein enhances the pathogenicity of group B streptococci in immune mice
Abstract
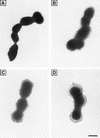
The alpha C protein is a protective surface-associated antigen of group B streptococci (GBS). The prototype alpha C protein of GBS (strain A909) contains nine identical tandem repeats, each comprising 82 amino acids, flanked by N- and C-terminal domains. Clinical isolates of GBS show variable numbers of repeats with a normal distribution and a median of 9 to 10 repeats. Here, we show that escape mutants of GBS expressing one-repeat alpha C protein were 100-fold more pathogenic than GBS expressing wild-type nine-repeat alpha C protein in neonatal mice whose dams were immunized with antiserum elicited to nine-repeat alpha C protein (50% lethal doses of 1.6 x 10(3) and 1.8 x 10(5), respectively; P = 0.0073). There was no difference in pathogenicity in nonimmune mice. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay inhibition showed that nine-repeat but not one-repeat alpha C protein is readily available for antibody binding on the surface of intact GBS. Immune electron microscopy studies with antibodies to the capsular polysaccharide (CPS) and to the alpha C protein demonstrated localization of the nine-repeat alpha C protein and the CPS at similar distances from the cell wall. The one-repeat alpha C protein was visualized poorly and only in close proximity to the cell wall, thus suggesting that antibody binding to the protein was hindered by CPS or other cell surface components. We concluded that deletion in the repeat region of the alpha C protein enhanced the pathogenicity of GBS in immune mice by (i) loss of a protective (conformational) epitope(s) and (ii) loss of antibody binding to the alpha C protein due to a decrease in antigen size relative to cell wall components and/or CPS.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Variation in repeat number within the alpha C protein of group B streptococci alters antigenicity and protective epitopes.Infect Immun. 1996 Sep;64(9):3576-83. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.9.3576-3583.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8751902 Free PMC article.
-
Group B streptococci escape host immunity by deletion of tandem repeat elements of the alpha C protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):4131-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4131. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8633028 Free PMC article.
-
Tandem repeat deletion in the alpha C protein of group B streptococcus is recA independent.Infect Immun. 2001 Aug;69(8):5037-45. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.5037-5045.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11447184 Free PMC article.
-
Surface Structures of Group B Streptococcus Important in Human Immunity.Microbiol Spectr. 2019 Mar;7(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0001-2017. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0001-2017. Microbiol Spectr. 2019. PMID: 30873933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcus agalactiae Non-Pilus, Cell Wall-Anchored Proteins: Involvement in Colonization and Pathogenesis and Potential as Vaccine Candidates.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 5;9:602. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00602. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29686667 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diversity and plasticity of the intracellular plant pathogen and insect symbiont "Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus" as revealed by hypervariable prophage genes with intragenic tandem repeats.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Sep;77(18):6663-73. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05111-11. Epub 2011 Jul 22. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21784907 Free PMC article.
-
Variation in the number of tandem repeats and profile of surface protein genes among invasive group B Streptococci correlates with patient age.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 May;45(5):1634-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00122-07. Epub 2007 Mar 7. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17344358 Free PMC article.
-
Mosaicism in the alpha-like protein genes of group B streptococci.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 15;97(17):9630-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.17.9630. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10944228 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope structure of the Bordetella pertussis protein P.69 pertactin, a major vaccine component and protective antigen.Infect Immun. 2004 Jul;72(7):3716-23. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.3716-3723.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15213111 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha C protein as a carrier for type III capsular polysaccharide and as a protective protein in group B streptococcal vaccines.Infect Immun. 1999 May;67(5):2491-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.5.2491-2496.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10225912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker C J, Edwards M S. Group B streptococcal infections. In: Remington J S, Klein J O, editors. Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant. 3rd Edition ed. Philadelphia, Pa: W.B. Saunders; 1990. pp. 742–811.
-
- Blake M S, Johnston H, Russell-Jones G J, Gotschlich E C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984;136:175–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

