Alteration of HLA-B27 peptide presentation after infection of transfected murine L cells by Shigella flexneri
- PMID: 9712804
- PMCID: PMC108542
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4484-4490.1998
Alteration of HLA-B27 peptide presentation after infection of transfected murine L cells by Shigella flexneri
Abstract
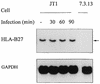
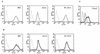
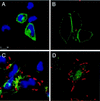
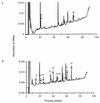
Shigella flexneri is a triggering agent for reactive arthritis in HLA-B27-susceptible individuals. Considering the intracellular multiplication of bacteria, it seems likely that bacterial peptides may be presented by the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I pathway. To examine this hypothesis, we infected HLA-B*2705- and/or human beta2-microglobulin-transfected murine L-cell lines with M90T, an invasive strain of S. flexneri. Bacterial infection induced no detectable modifications in the biosynthesis and expression level of HLA-B27, as assessed by immunoprecipitation, Northern blot analysis, and flow cytometry. Using confocal microscopy, we observed that bacterial infection induced a clustering of HLA-B27 molecules during macropinocytosis and before bacterial dissemination from cell to cell. Peptides naturally bound to HLA-B27 molecules were acid eluted from infected cells and separated by high-performance liquid chromatography. Major differences were observed in high-performance liquid chromatography profiles and in the nature of peptides presented following bacterial infection. Although most of the antigens presented were not accessed by Edman degradation, we obtained two sequences partially homologous to bacterial proteins. These peptides lacked the major HLA-B27 peptide anchor (Arg) at position 2, and one had an unusual length of 14 amino acids. These data suggest that alterations in the peptide presentation by HLA-B27 occur during infection, which could be relevant to the pathogenesis of HLA-B27-related arthritis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of infection of cells with bacteria associated with reactive arthritis on the peptide repertoire presented by HLA-B27.J Med Microbiol. 2001 Apr;50(4):385-389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-4-385. J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11289525
-
HLA-B27 modulates the survival of Salmonella enteritidis in transfected L cells, possibly by impaired nitric oxide production.Infect Immun. 1997 Oct;65(10):4236-42. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.10.4236-4242.1997. Infect Immun. 1997. PMID: 9317032 Free PMC article.
-
A high incidence of Shigella-induced arthritis in a primate species: major histocompatibility complex class I molecules associated with resistance and susceptibility, and their relationship to HLA-B27.Immunogenetics. 2000 Apr;51(4-5):314-25. doi: 10.1007/s002510050625. Immunogenetics. 2000. PMID: 10803844
-
Presentation of HLA class I-derived peptides: potential involvement in allorecognition and HLA-B27-associated arthritis.Immunol Rev. 1996 Dec;154:137-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1996.tb00932.x. Immunol Rev. 1996. PMID: 9034866 Review.
-
HLA-B27 and disease: a consequence of inadvertent antigen presentation?Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1992 Feb;18(1):11-21. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1992. PMID: 1561398 Review.
Cited by
-
T-cell studies in the spondyloarthropathies.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2000 Aug;2(4):297-305. doi: 10.1007/s11926-000-0066-y. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2000. PMID: 11123074 Review.
-
A molecular insight on the association of HLA-B27 with spondyloarthropathies.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 1999 Oct;1(1):78-85. doi: 10.1007/s11926-999-0029-x. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 1999. PMID: 11123019 Review.
-
Enterobacterial infection modulates major histocompatibility complex class I expression on mononuclear cells.Immunology. 1999 Jul;97(3):420-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00803.x. Immunology. 1999. PMID: 10447763 Free PMC article.
-
Sampling of major histocompatibility complex class I-associated peptidome suggests relatively looser global association of HLA-B*5101 with peptides.Hum Immunol. 2006 Nov;67(11):894-906. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2006.08.294. Epub 2006 Sep 20. Hum Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17145369 Free PMC article.
-
Use of HLA-B27 tetramers to identify low-frequency antigen-specific T cells in Chlamydia-triggered reactive arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(6):R521-34. doi: 10.1186/ar1221. Epub 2004 Sep 23. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004. PMID: 15535830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beatty P R, Stephens R S. CD8+ T lymphocyte-mediated lysis of Chlamydia-infected L cells using an endogenous antigen pathway. J Immunol. 1994;153:4588–4595. - PubMed
-
- Benjelloun-Touimi Z, Sansonetti P J, Parsot C. SepA, the major extracellular protein of Shigella flexneri: autonomous secretion and involvement in tissue invasion. Mol Microbiol. 1995;17:123–135. - PubMed
-
- Boisgérault, F., D. Charron, and A. Toubert. 1997. Unpublished data.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

