Elevated concentrations of eotaxin and interleukin-5 in human neurocysticercosis
- PMID: 9712812
- PMCID: PMC108550
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.9.4522-4525.1998
Elevated concentrations of eotaxin and interleukin-5 in human neurocysticercosis
Abstract
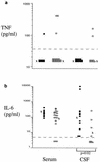
Symptomatic neurocysticercosis, a major cause of epilepsy worldwide, results from inflammation around Taenia solium larvae, but the mechanisms are unknown. Eotaxin, not previously reported in cases of human infection, and interleukin-5 (IL-5) but not IL-8 concentrations were elevated in patient serum, and IL-5 levels were also elevated in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Eosinophil-selective mediators may be involved in the pathogenesis of cysticercosis. IL-6 concentrations were also elevated in patient CSF, possibly indicative of an acute-phase response.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bronchial interleukin-5 and eotaxin expression in nasal polyposis. Relationship with (a)symptomatic bronchial hyperresponsiveness.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001 Apr;163(5):1226-32. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.5.2004197. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001. PMID: 11316663
-
Elevated levels of eotaxin and interleukin-5 in blister fluid of bullous pemphigoid: correlation with tissue eosinophilia.Br J Dermatol. 2000 Jul;143(1):112-6. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2000.03599.x. Br J Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 10886144
-
Eotaxin triggers eosinophil-selective chemotaxis and calcium flux via a distinct receptor and induces pulmonary eosinophilia in the presence of interleukin 5 in mice.Mol Med. 1996 May;2(3):334-48. Mol Med. 1996. PMID: 8784786 Free PMC article.
-
Eotaxin and eosinophil recruitment: implications for human disease.Mol Med Today. 2000 Jan;6(1):20-7. doi: 10.1016/s1357-4310(99)01635-4. Mol Med Today. 2000. PMID: 10637571 Review.
-
IL-4 induces eotaxin in human dermal fibroblasts.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999;120 Suppl 1:19-23. doi: 10.1159/000053587. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10529597 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunology of Taenia solium taeniasis and human cysticercosis.Parasite Immunol. 2014 Aug;36(8):388-96. doi: 10.1111/pim.12126. Parasite Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24962350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of eotaxin expression and release from human airway smooth muscle cells by IL-1beta and TNFalpha: effects of IL-10 and corticosteroids.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Jul;127(5):1145-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702660. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10455260 Free PMC article.
-
Distinctive cytokine, chemokine, and antibody responses in Echinococcus multilocularis-infected patients with cured, stable, or progressive disease.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2014 Jun;203(3):185-93. doi: 10.1007/s00430-014-0331-8. Epub 2014 Feb 9. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24509604
-
Do helminths cause epilepsy?Parasite Immunol. 2009 Nov;31(11):697-705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2009.01128.x. Parasite Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19825109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The implantation of Taenia solium metacestodes in mice induces down-modulation of T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.Parasitol Res. 2005 Mar;95(4):256-65. doi: 10.1007/s00436-004-1285-3. Epub 2005 Jan 28. Parasitol Res. 2005. PMID: 15678353
References
-
- Ali-Khan Z, Siboo R, Meerovitch E, Faubert G, Faucher M G. Cysticercosis racemosus in an eosinophilic phlegmon in the brain. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1981;75:774–779. - PubMed
-
- Aloisi F, Care A, Borsellino G, Gallo P, Rosa S, Bassani A, Cabibbo A, Testa U, Levi G, Peschle C. Production of hemolymphopoietic cytokines (IL-6, IL-8, colony-stimulating factors) by normal human astrocytes in response to IL-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1992;149:2358–2366. - PubMed
-
- Amiri P, Locksley R M, Parslow T G, Sadick M, Rector E, Ritter D, McKerrow J H. Tumour necrosis factor α restores granulomas and induces parasite egg-laying in schistosome-infected SCID mice. Nature. 1992;356:604–607. - PubMed
-
- DeForge L E, Remick D G. Sandwich ELISA for detection of picogram quantities of interleukin-8. Immunol Investig. 1991;20:89–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

